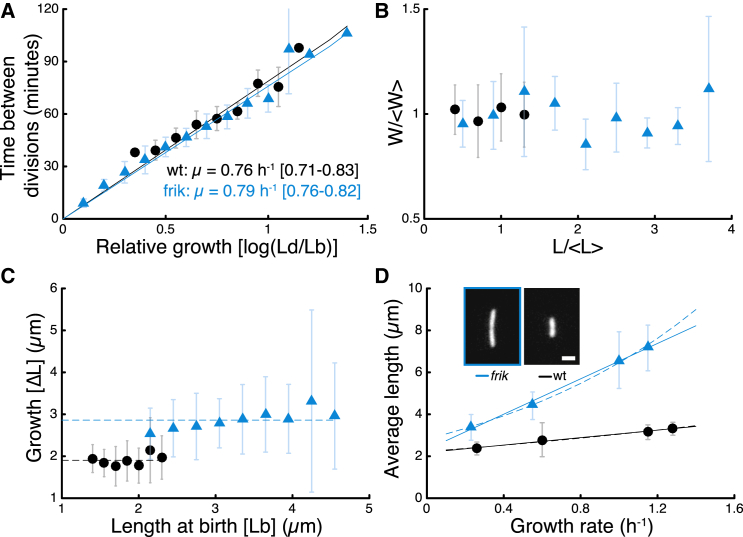
Figure 1.
Cell-size regulation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its elongated mutant frik. (A) Correlation between relative growth (log(Ld/Lb)) and time between divisions reveals identical growth rates in both strains. Binned data. (B) Cell width in exponential growth is independent of cell length in both wild-type and frik (Pearson correlation coefficient: 0.061 (wt) and −0.039 (frik)). Data are rescaled by average length and width for each strain. Average cell length is 3.14 μm for wt and 5.60 μm for frik. Average cell width is 0.75 μm for wild-type and 0.74 μm for frik (p = 0.58, N = 117 for wild-type and N = 107 for frik). (C) There is no correlation between growth from birth to division (ΔL = Ld-Lb) and length at birth Lb (Pearson correlation coefficient: −0.010 (wt) and 0.114 (frik)). (D) Cell lengths measured in exponential growth in different liquid media show that wild-type and frik follow the growth law. Media used were (from slowest to fastest) minimal glycerol media, minimal glucose media, casamino acid media, and LB. Error bars are 25 and 75% percentiles. Linear fits (solid lines) are L = 0.89 μ + 2.18 (μm) for wt, L = 4.21 μ + 2.32 (μm) for frik. Exponential fits (dashed lines) are L = 2.22 exp(0.32 μ) (μm) for wt, L = 2.82 exp(0.83 μ) (μm) for frik. (Inset) Micrographs of a frik cell (left) and a wt cell (right) in casamino acid media, imaged by fluorescence microscopy. Scale bar: 2 μm. To see this figure in color, go online.