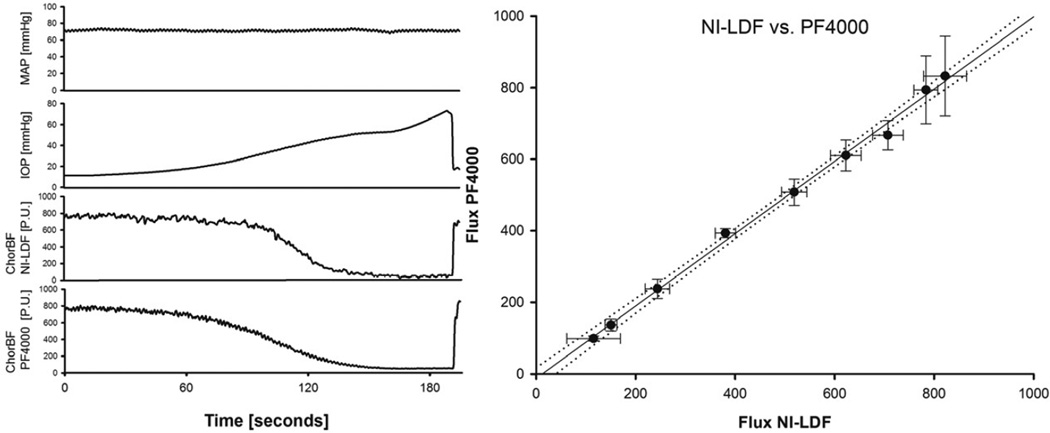
Figure 6. Comparison of both instruments in a rabbit model.
Left panel: Representative tracing of a single experiment of the IOP protocol. MAP, IOP and the flux signals of both instruments were recorded simultaneously. Note that the two instruments were directed at different measurement spots and utilize different wavelengths. The IOP was increased by infusion of saline to lower the ocular perfusion pressure (OPP = MAP – IOP), the MAP remained constant Right panel: Response of the NILDF plotted against the PF4000 during increase of IOP (n=5). Each data point represents the average flow (± standard deviation) over a 5 mmHg bin of perfusion pressure. The equation of the regression line is y=1,01*x −12,54 P.U., the correlation coefficient 0.99, the standard error of the estimate = 17,54 P.U. (2% of the total range).