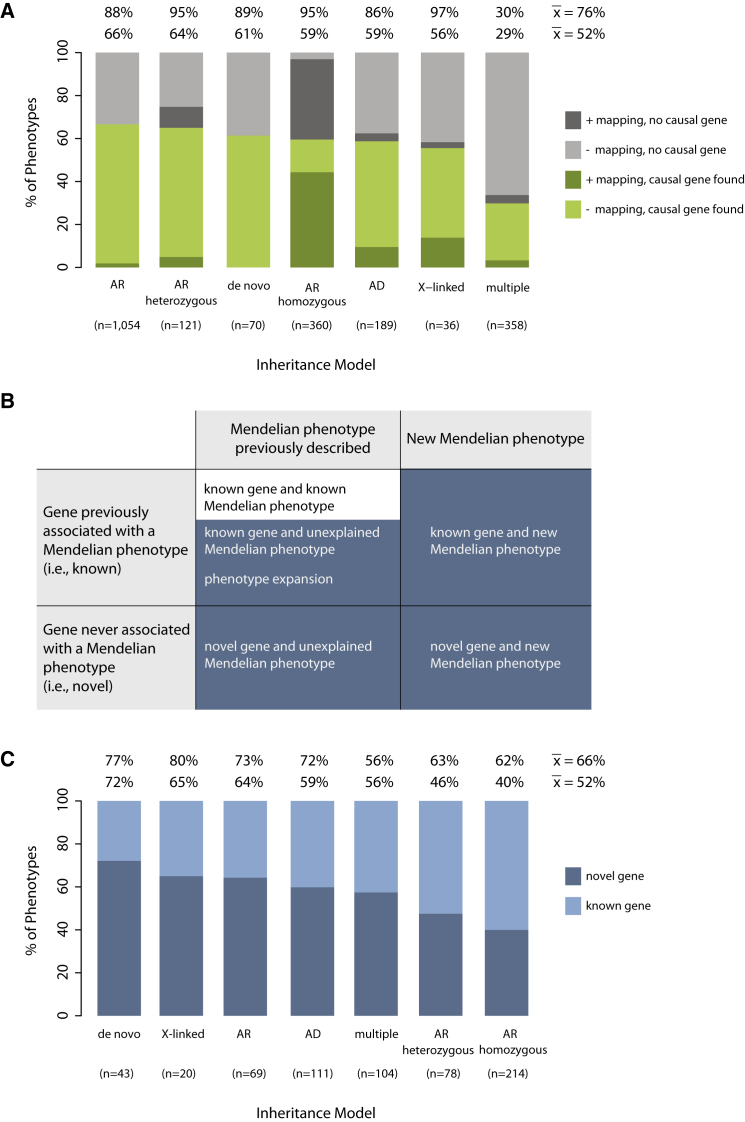
Figure 9.
Discovery Metrics under Different Models of Inheritance for Mendelian Phenotypes Studied by the CMGs
(A) The percentage of Mendelian phenotypes for which a gene was discovered on the basis of conservative causality criteria per different models of inheritance with mapping data (dark green) or without mapping data (light green) is shown. Also shown is the percentage of Mendelian phenotypes for which a causal gene was not found per different models of inheritance with mapping data (dark gray) or without mapping data (light gray). Note that for most phenotypes analyzed under an autosomal-recessive homozygous model that failed, mapping data were available; however, the statistical significance of the mapping data varied (e.g., number and length of runs of homozygosity, magnitude of LOD score, etc.). The mean number of genes discovered per Mendelian phenotype was 0.52 or 0.76 on the basis of only conservative or combined conservative and suggestive criteria, respectively. These figures do not include results from persons found to have more than one Mendelian phenotype.
(B) Classification of discoveries of genes underlying Mendelian phenotypes as known (white squares) or novel (blue squares).
(C) Percentage of Mendelian phenotypes for which a novel discovery (dark blue) or known discovery (light blue) was made on the basis of conservative causality criteria per different models of inheritance. The mean number of novel discoveries per Mendelian phenotype was 0.52 or 0.66 on the basis of only conservative or combined conservative and suggestive criteria, respectively.
Abbreviations are as follows: AD, autosomal dominant; AR, autosomal recessive (when recessive inheritance was clear, but analysis of both consanguineous and non-consanguineous families contributed to the discovery); AR homozygous, autosomal recessive in a consanguineous family; AR heterozygous, autosomal recessive in a non-consanguineous family (i.e., compound-heterozygous mutations).