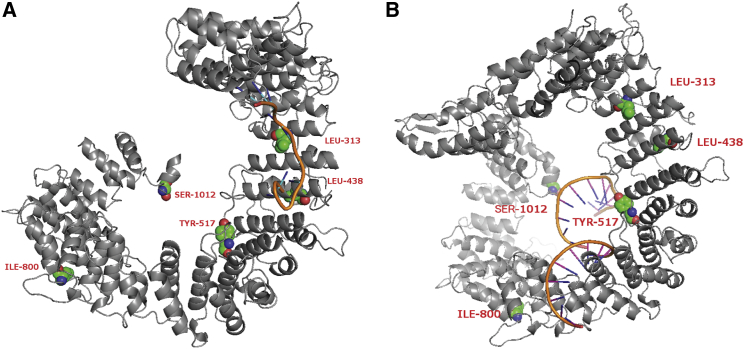
Figure 4.
Models of the Predicted Complex Structure of the THOC2-RNA Complex
(A) Complex structure was built on the basis of the template 1m8y. Variants p.Leu313Phe and p.Leu438Pro are located in mRNA-binding sites.
(B) Complex structure was built on the basis of the template 3a6p. Variant Tyr517Cys is in an mRNA-binding site.
The workflow used for predicting the THOC2-RNA interaction is shown (Figure S4). First, the sequence of THOC2 was analyzed by SPARKS-X, which predicts several potential protein structures. Then, the best structure model was compared to a library of 1,164 RNA-binding proteins, and the two best-aligned complex-structure models were generated on the basis of chains 3a6pA and 1m8yA by SPalign28 and had SP-scores of 0.68 and 0.65, respectively. A score > 0.5 indicates homologous structures, which were selected for building the complex models. From the complex models, a protein residue and a RNA base were considered in contact if the shortest distance between any pair of heavy atoms from them was within 4.5Å. For the first complex structure, variants p.Leu313Phe and p.Leu438Pro were located in the mRNA-binding domain, but p.Leu313Phe interacted with RNA. The other two variants, p.Ile800Thr and p.Ser1012Pro, were located on another domain, which was annotated with DNA-binding function by Pfam.29