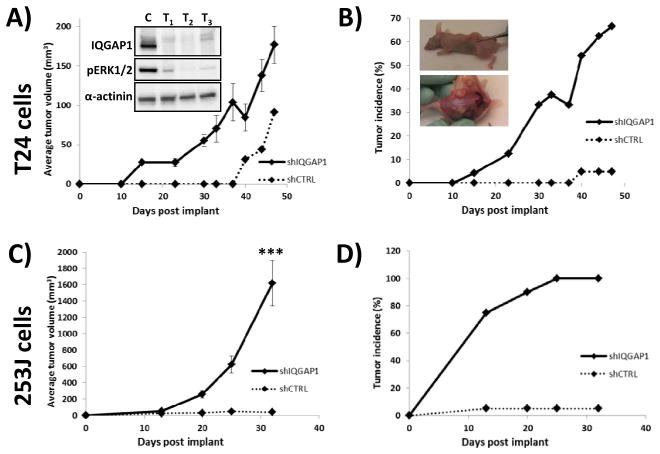
Fig. 3. IQGAP1 knockdown leads to dramatic increases in tumor outgrowth in vivo.
(A) In validation of the screening results, T24 cells expressing IQGAP1 shRNA exhibit significant increases in tumor outgrowth after subcutaneous injection in mice. Analysis of all the tumors following animal sacrifice at day 47 post-implant confirmed continued knockdown of IQGAP1 (inset). Consistent with the literature, depletion of IQGAP1 also lead to a decrease in activated Erk (inset). As the shCTRL cells only produced 1 tumor, statistics cannot be performed. (B) Not only does loss of IQGAP1 in T24 cells increase tumor growth rate and volume but also increases the % of tumor incidence to a rate of nearly 70% by day 47, relative to only 10% for control cells. The inset necropsy picture illustrates representative tumors in mice at time of harvest. (C–D) The ability of IQGAP1 depletion to promote tumor outgrowth and incidence is even more dramatic in 253J cells. In 253J cells the experiment was halted at 32 weeks at which point there was a 100% tumor take with shIQGAP1 cells. *** p<0.001.