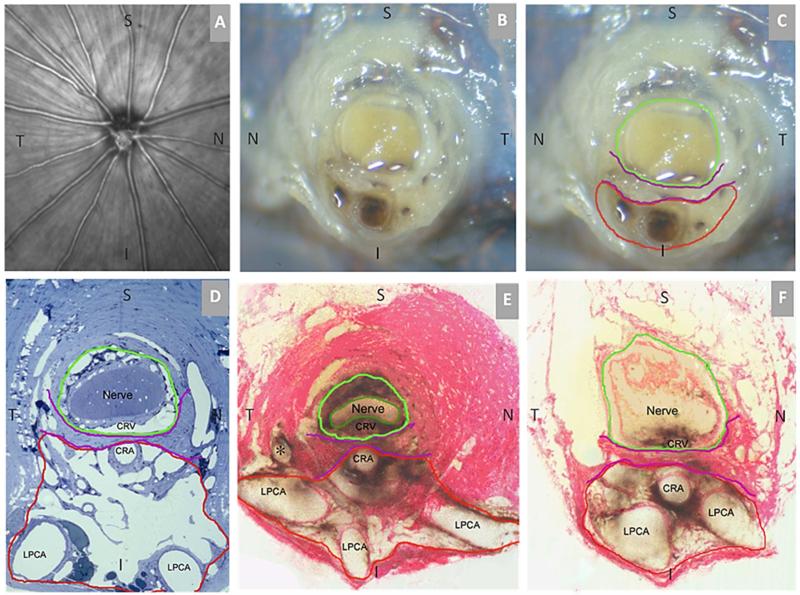
Figure 1. Rat Optic Nerve Head Macroscopic and Microscopic Relationships I – Transverse Sections.
(A) 30 degree SDOCT Infrared Reflectance image of the rat optic disc (the vitreal surface of the optic nerve head) (courtesy of Brad Fortune). (B) Macroscopic appearance of the cut surface of the rat optic nerve just posterior to the scleral shell (view from the back of the eye). (C) Principal macroscopic relationships: 1) the neurovascular bundle (green); and the more-inferior 2) arterial bundle (red); are separated by a sling of scleral tissues 3) the scleral sling, (purple) (view from the back of the eye). (D-E) Principal scleral openings. Unlike the primate, there are two principal openings within the sclera of the rat ONH: 1) the neurovascular canal (green) and the more-inferior arterial opening (red), which is not a well-defined canal, being irregular due to the choroidal branches of the LPCAs (D and E) and separated from the neurovascular canal by the scleral sling (purple). Unlike the primate, which has on average 15 short posterior ciliary arteries that are evenly distributed around the circumference of the scleral canal, the inferior concentration of the LPCAs and the density of their intrascleral branches to the choroid combined with the actual CRA canal (D – F) suggest an “effective” second opening in the sclera. (D) Transverse histologic section through the scleral portion of the optic nerve head demonstrating the same relationships seen posterior to the globe in panels B and C. Note that the neurovascular bundle consists of the optic nerve surrounded by a vascular plexus within the inferior portion of which runs the CRV. The arterial bundle is made up of the central retinal artery, the two main LPCAs and their intrascleral branches to the choroid (vascular spaces in between the principal arteries - not labeled). (E) A digital transverse section image from a histomorphometric reconstruction demonstrating the same relationships as (D). (F) Digital section image from the same eye just posterior to the globe and close to the view seen macroscopically in (C). The intrascleral (E) and retrobulbar short posterior ciliary arteries (F) are branches of the LPCAs rather than the Ophthalmic Artery. A preferential superior-temporal course of the optic nerve and neurovascular bundle as they pass through the sclera into the orbit are suggested by comparing the green circle in (F) to (E). CRV- Central retinal vein, LPCAs- Long Posterior Ciliary Arteries. N – Nasal; T – Temporal; I –Inferior; S – Superior.