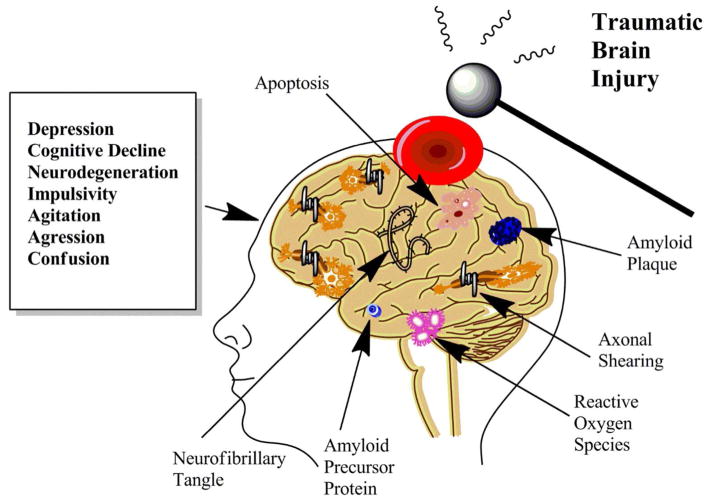
Figure 5.
The Chronic Effects of Traumatic Brain Injury. Some individuals experiencing TBI are more susceptible to chronic effects than others. Environmental and genetic factors play a role. Pathologic changes that may develop include neurofibrillary tangles, axonal shearing, and amyloid plaques to name a few. Neuropsychiatric symptoms may also develop such as depression, impulsivity, cognitive decline, and confusion. This area of chronic deficits following TBI is a topic of growing importance receiving renewed research focus and funding.