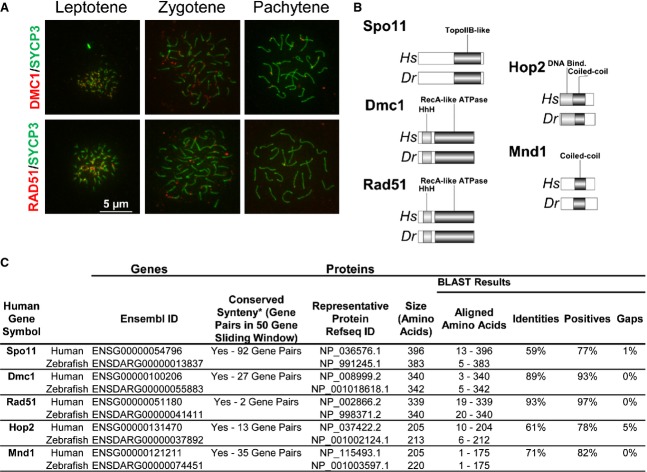
Figure 5.
Zebrafish as a model for meiotic recombination studies. (A) Visualization of Dmc1 and Rad51 loading at chromosomal recombination sites. The methodologies used for chromosome surface spreading of zebrafish spermatocytes and immunolabeling are similar to those previously described for mouse spermatocytes 70,96. Sources and dilutions of primary antibodies used are as follows. Rabbit anti-Rad51 serum (H-92; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, USA), produced against an epitope corresponding to amino acids 1–92 of Rad51 of human origin (84% identity to the zebrafish Rad51 protein sequence), was used at a dilution of 1 : 100. Goat anti-Dmc1 serum (C-20; Santa Cruz Biotechnology), produced against an epitope corresponding to amino acids 290–340 of Dmc1 of human origin (90% identity to the zebrafish Dmc1 protein sequence), was used at a dilution of 1 : 100. Mouse anti-SYCP3 (Novus, Littleton, CO, USA) was used at a dilution of 1 : 400. Secondary antibodies were obtained from Jackson IR Laboratories (West Grove, PA, USA) and were used at a dilution of 1 : 300. Slides were counterstained using Vectashield mounting solution (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA, USA) containing 2 μg·mL−1 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). All images were acquired using a 40× objective oil immersion lens. We used an Axiovision SE 64 microscope (Zeiss, Thornwood, NY, USA) for imaging acquisition and processing. Scale bar = 5 μm for all images. (B) Structural conservation of proteins acting in homologous recombination in human and zebrafish. (C) Conservation of HR effectors between human and zebrafish.