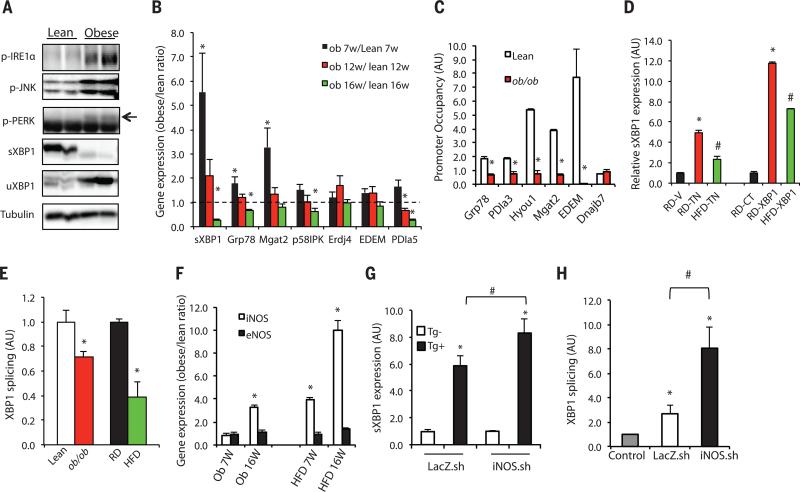
Fig. 1. Inflammation contributes to defective IRE1α-mediated XBP1 splicing in obese liver.
(A) UPR status was examined in livers of 16-week-old obese (ob/ob) and lean mice by using phosphorylation of IRE1α, PERK, and JNK, as well as expression of sXBP1 and uXBP1 as markers. Data are representative of results from two to three independent cohorts of mice. (B) Expression of hepatic UPR modulators in 7-, 12- and 16-week-old ob/ob mice relative to lean controls (dashed line indicates lean level), n = 4. (C) ChIP assay examining XBP1 target gene occupancy in primary hepatocytes from 16-week-old ob/ob and lean mice. Data were normalized to 2% input, followed by comparison to each immunoglobulin G (IgG) control (n = 4). Data are representative of results from two independent sets of mice. Asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance between lean and obese mice in (B) and (C). Statistical analysis was performed by multiple t tests and significance was determined by the Holm-Šídák method using Prism (B) and Student's t test (C). AU, arbitrary units. (D) sXBP1 was examined in the livers from lean (RD) and obese (HFD-fed) mice injected with vehicle (V), or tunicamycin (TN, 6 hours, 0.5 mg/kg per kg body weight). sXBP1 expression was also examined in the livers from control mice fed RD or HFD transduced with full-length XBP1 (RD-XBP1, HFD-XBP1) or lean controls (RD-XBP1). Asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance between treatments within the control group, and # indicates statistical significance between RD and HFD [one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by post hoc Tukey's test], n = 6 to 8 mice. (E) In vitro splicing assays measuring the XBP1 splicing efficiency using hepatic IRE1α from mice with dietary (HFD) and genetic (ob/ob) obesity and controls. sXBP1 expression was examined by qRT-PCR. Results are normalized to lean samples. Asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance between lean and obese mice (Student's t test, n = 3). Data are representative of results from two independent sets of mice. (F) iNOS and eNOS mRNAs were examined in livers of 7- and 16-week-old ob/ob or HFD-fed mice and lean controls by qRT-PCR. Asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance between lean and obese mice (Student's t test), n = 4 to 6. (G) sXBP1 expression was examined by qRT-PCR in primary hepatocytes from lean mice transduced with Ad-shiNOS (iNOS.sh) or control virus (LacZ.sh) followed by treatment with thapsigargin (Tg+) for 2 hours, n = 4. (H) In vitro XBP1 splicing assay using IRE1α purified from the livers ob/ob mice after iNOS suppression (normalized to IgG control). Asterisk (*) indicates statistical significance between treatments and controls, and # indicates statistical significance between iNOS.sh group and LacZ.sh group (one-way ANOVA followed by post hoc Tukey's test). All data are shown as means ± SEM. Data are representative of results from two independent sets of mice. *P < 0.05; #P < 0.05.