Fig. 5. Cross-subtype HIV neutralization by CLIN-directed IgG JL427 and comparison with its V-domain identical IgM counterpart.
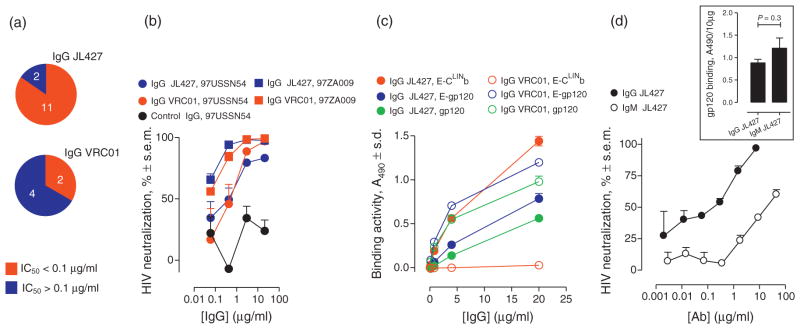
(a) Cross-subtype HIV neutralization. IgG JL427-neutralized CCR5-dependent and CXCR4-dependent primary HIV strains across subtypes A, B, C, D and AE. For comparison, six IgG JL427-sensitive strains were analyzed for neutralization by reference IgG VRC01 directed to an outer domain CD4-binding site epitope. Red and blue pie sections represent strains neutralized with IC50 below 0.1 μg/ml or above 0.1 μg/ml, respectively (Supplemental Table S6, http://links.lww.com/QAD/A552). (b) Example IgG JL427 and IgG VRC01 neutralization data (subtype C strain 97ZA009 and subtype A strain 97USSN54). The control IgG is an irrelevant antibody with the same isotype as IgG JL427. (c) Binding of E-CLINb, E-gp120 and gp120 by IgG JL427. IgG VRC01 was devoid of E-CLINb binding activity and the control isotype matched IgG did not bind any test probe (A490<0.05). (d) HIV neutralization by IgM and IgG JL427 containing the same V-domains (subtype C strain 97ZA009). IC50 values for the IgM and IgG, respectively, 19.7 and 0.05 μg/ml. Inset, gp120 binding by IgM and IgG JL427.
