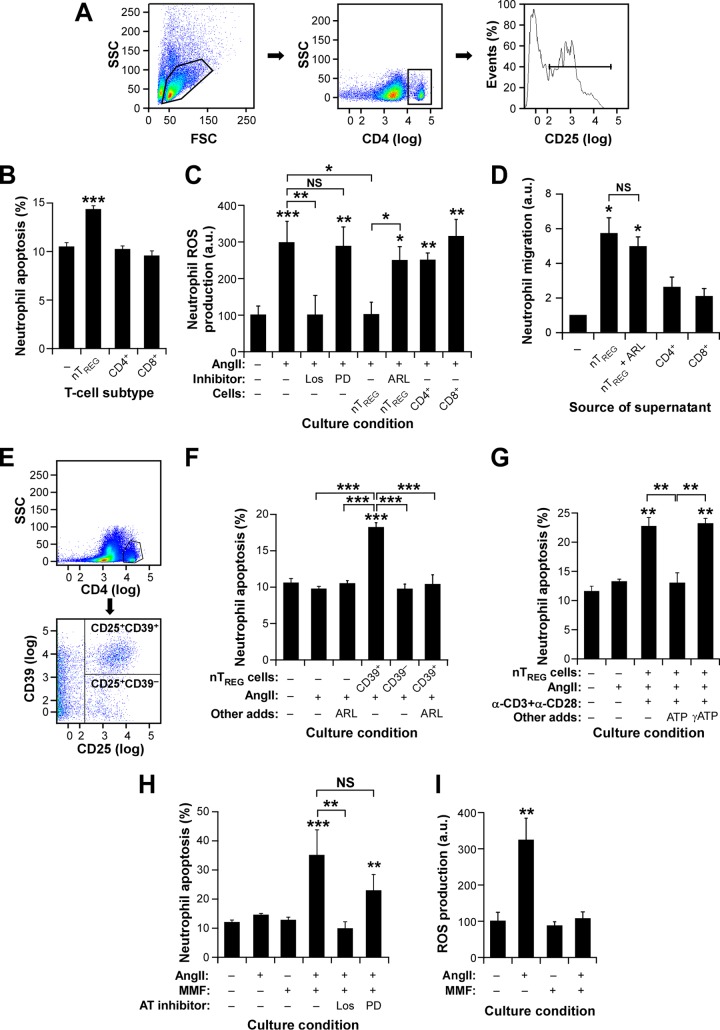
FIG 8.
TREG cells induce CD39-dependent neutrophil apoptosis. (A) Example of the flow cytometry purification step for obtaining the splenic CD4+ CD25+ nTREG cells used in the experiments for which results are shown in panels B to D. (B and C) Apoptotic response (B) and ROS production (C) of neutrophils under the indicated in vitro conditions. ARL, ARL 67156; CD4+, CD4+ CD25− T cells; CD8+, CD8+ T cells; Los, losartan; PD, PD123319. Asterisks indicate significant differences (*, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001) from the control or between the indicated experimental groups (n = 4). (D) Effect of TREG cell-derived culture supernatants on neutrophil chemotaxis (values obtained with medium alone were given an arbitrary value of 1). Asterisks indicate significant differences (*, P ≤ 0.05) from the control; NS, no significant difference (n = 4). (E) Example of the purification step used to obtain the splenic CD39+ and CD39− nTREG cells used in the experiment for which results are shown in panel F. (F to H) Apoptotic responses of neutrophils under the indicated culture conditions. CD39+, CD4+ CD25+ CD39+ nTREG cells; CD39−, CD4+ CD25+ CD39− nTREG cells; α-CD3 and α-CD28, antibodies to mouse CD3 and CD28, respectively. Asterisks indicate significant differences (**, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001) from the control or between the indicated experimental groups (n = 4). (I) AngII-stimulated ROS production by neutrophils under the indicated culture conditions. Asterisks indicate significant differences (**, P ≤ 0.01) from the control (n = 4).