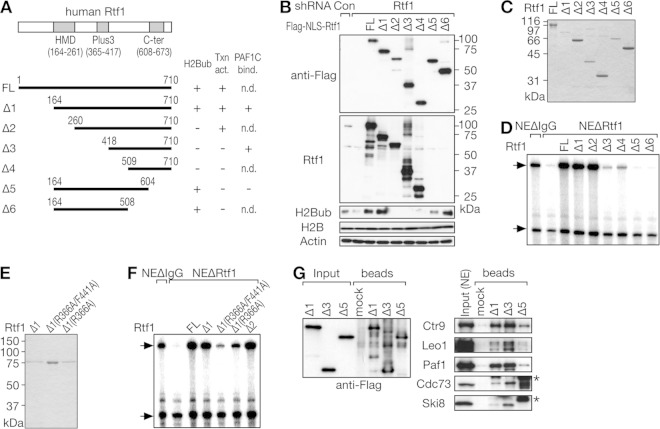
FIG 4.
Distinct structural requirements for human Rtf1 in H2B monoubiquitination and transcriptional activation in vitro. (A) Schematic structures of human Rtf1 deletion mutants. The results shown in panels B to G are summarized on the right. Txn act., transcriptional activation; PAF1C bind., PAF1C binding; n.d., not determined. (B) Knockdown-rescue experiments. HeLa cells were sequentially infected with a lentiviral vector for shRNA targeting Rtf1 and transfected with one of the Flag-NLS-Rtf1 expression vectors carrying shRNA-resistant mutations. Cells were harvested 7 days postinfection (3 days posttransfection) and subjected to immunoblot analysis. (C and E) The purity of full-length (FL) Flag-Rtf1 prepared from insect cells and His-Rtf1-Flag deletion mutants prepared from bacteria was examined by Coomassie blue staining. (D and F) The transactivation potential of Rtf1 mutants was examined by in vitro transcription assays using NEΔRtf1. (G) The indicated Rtf1 mutants were first adsorbed onto anti-Flag-agarose beads and then incubated with HeLa cell NE. Input and bound fractions were analyzed by immunoblotting. The asterisks denote nonspecific signals.