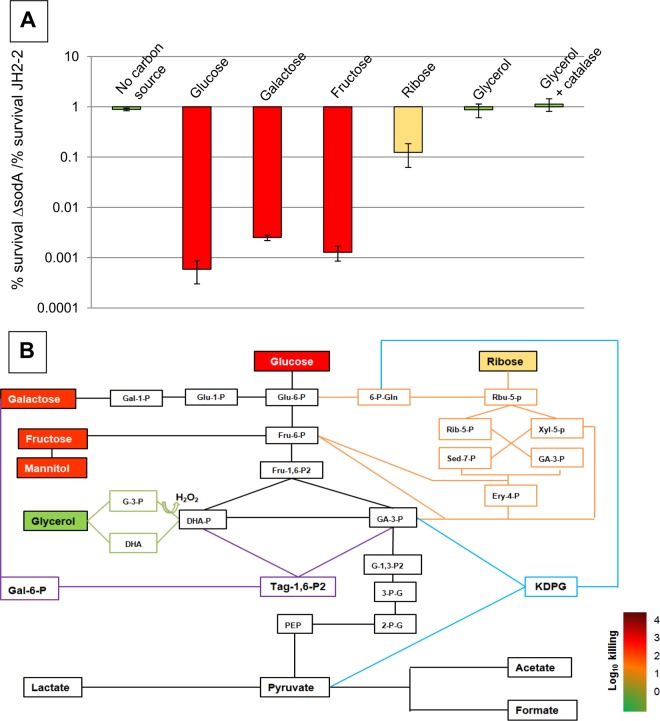
FIG 2.
Bactericidal activity is dependent on the energy source in the E. faecalis JH2-2 ΔsodA mutant. (A) Ratio of relative survival rates of the E. faecalis ΔsodA mutant and the E. faecalis JH2-2 wild-type strain after 24 h of exposure to 20 μg/ml of vancomycin in ccM17 MOPS medium supplemented with glucose, galactose, fructose, ribose, or glycerol. In the case of glucose, ribose, and glycerol supplementation, similar results in the presence of 20 μg/ml of penicillin have been obtained (see Fig. S2 in the supplemental material). Mean values of the results of at least three different experiments are represented with error bars indicating standard deviations. (B) Integration of the results determined as described for panel A into the metabolic network of E. faecalis. Metabolites are color-coded according to the degree of killing by vancomycin. The following metabolic intermediates are shown: glucose-6-phosphate (Glu-6-P), glucose-1-phosphate (Glu-1-P), fructose-6-phosphate (Fru-6-P), fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (Fru-1,6-P2), galactose-1-phosphate (Gal-1-P), galactose-6-phosphate (Gal-6-P), tagatose-1-6 bisphosphate (Tag-1,6-P2), glycerol-3-phosphate (G-3-P), dihydroxyacetone (DHA), dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHA-P), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (GA-3-P), 1,3-bisphospho-glycerate (G-1,3-P2), 3-phospho-glycerate (3-P-G), 2-phospho-glycerate (2-P-G), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), ribulose-5-phosphate (Rbu-5-P), ribose-5-phosphate (Rib-5-P), xylulose-5-phosphate (Xyl-5-P), erythrose-4-phosphate (Ery-4-P), sedoheptulose-7-phosphate (Sed-7-P), 6-phospho-gluconate (6-P-Gln), and 2-keto-3-deoxy-6-phosphogluconate (KDPG).