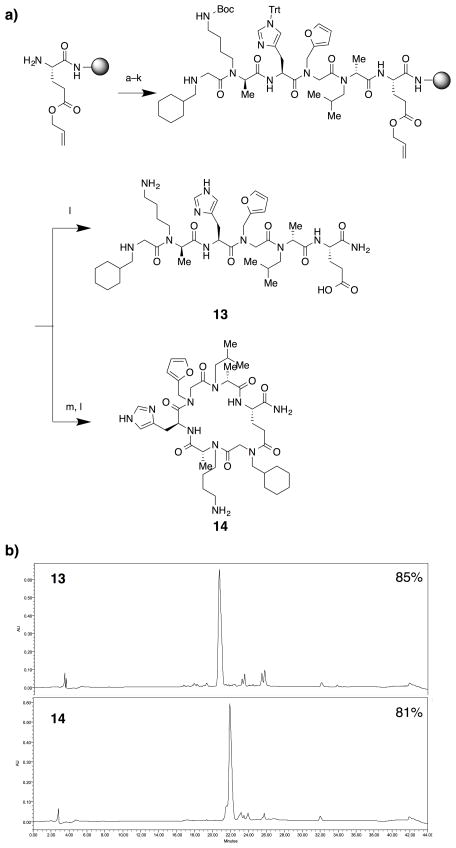
Fig. 4.
Synthesis of a pair of linear and macrocyclic N-alkylated peptides, 13 and 14. a) A scheme of the synthesis. Reaction conditions: a. R-BPA, BTC, DIPEA, and TMP in tetrahydrofurane (THF); b. 1 M piperonylamine in DMF; c. Chloroacetyl chloride, DIPEA, and TMP in DCM; d. 1 M isopentylamine in DMF; e. Fmoc-Asn(Trt)-OH, Oxyma, and DIC in DMF; f. 20% piperidine in DMF; g. R-BPA, BTC, DIPEA, and TMP in THF; h. 1 M N-boc-1,4-butanediamine in DMF; i. Chloroacetyl chloride, DIPEA, and TMP in DCM; j. 1 M 2-methoxyethylamine in DMF; k. tetrakis(triphenylphosphine)palladium (Pd(PPh4)) and Phenylsilane (PhSiH3) in DCM. l. 92.5% TFA, 2.5% triisopropylsilane (TIPS), 2.5% thioanisole, and 2.5% H2O; m. PyAOP, HOAt, and DIPEA in DMF. b) HPLC chromatograms of linear oligomer 13 (top) and cyclic oligomer 14 (bottom). Purities of desired compounds are labeled on top-right of chromatograms.