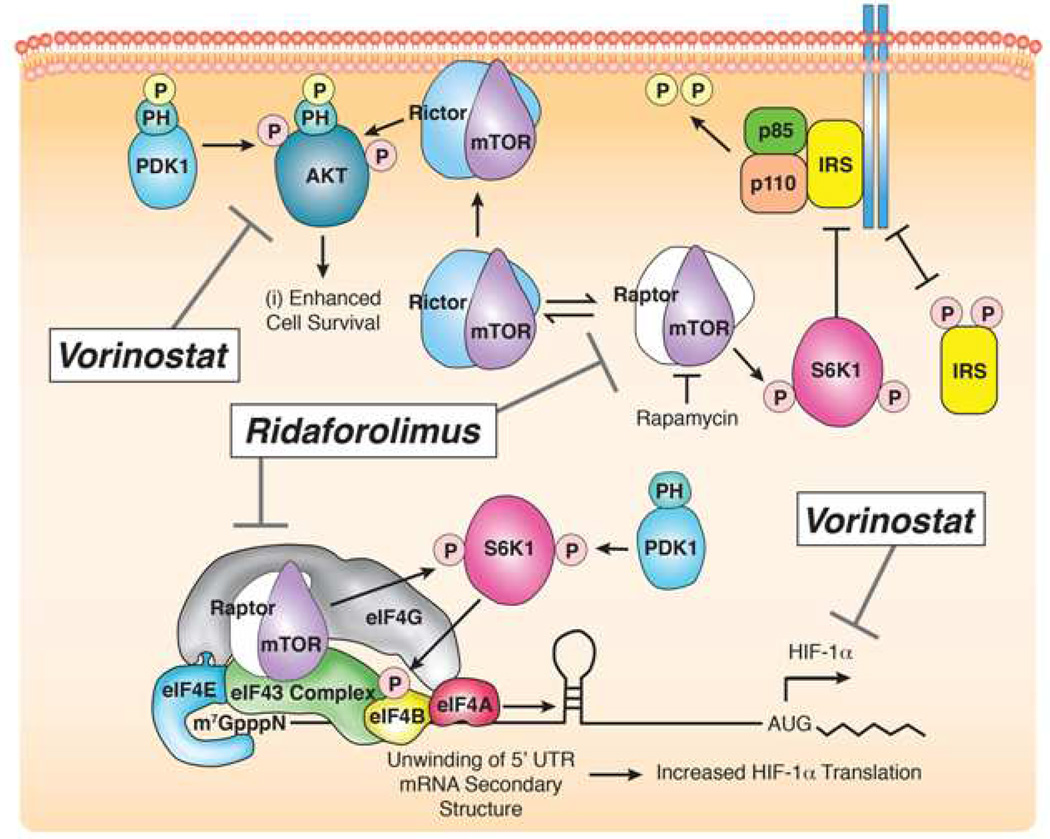
Figure 1. Mechanism of action of ridaforolimus and vorinostat on the mTOR pathway.
Pictorial depiction of the key proteins affected via altered transcription and translation by the mTOR inhibitor ridaforolimus and the HDAC inhibitor vorinostat. Ridaforolimus binds mTOR at the rapamycin binding domain resulting in allosteric kinase inhibiton and leading to downregulation of various cell cycle regulators as well as HIF-1. Vorinostat exerts its effects on histone deacetylation to decrease transcription, culminating in decreased pAkt and HIF-1.
Note: PDK, phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1; mTOR, mammalian target of rapamycin; S6K1, S6 kinase 1; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; eIF, eukaryotic initiation factor; HIF, hypoxia inducible factor