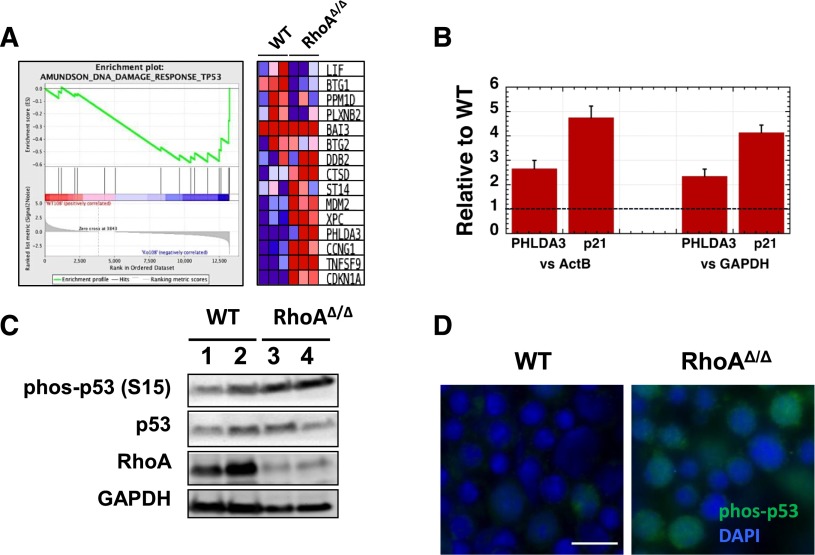
Figure 7.
DNA damage in RhoAΔ/Δ fetal liver erythroblasts leads to p53 and caspase activation. (A) Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) from RNA-Seq data of CD71+ cells isolated from E13.0 WT and RhoAΔ/Δ fetal livers (n = 3 for each genotype) demonstrating upregulation of p53-related DNA damage response genes39 in the RhoA-deficient erythroblasts. (B) The upregulation of PHLDA3 and p21 (CDKN1A) mRNA found by RNA-Seq was confirmed using RT-PCR on RNA isolated from CD71+ cells from E13.0 WT and RhoAΔ/Δ fetal livers (n = 3 for each genotype). Data are represented as mean ± SEM of fold-expression relative to WT; expression normalized vs Actin-B and vs glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) is shown. (C) Increased p53 phosphorylation at Ser-15 is demonstrated by western blotting in CD71+ cells isolated from E13.0 RhoAΔ/Δ fetal livers compared with WT. (D) Immunostaining on fetal liver touch-preps further confirmed increased phosphorylation of p53 phosphorylated at Ser-15 in E13.0 RhoAΔ/Δ fetal liver cells. The scale bar represents 10 µm.