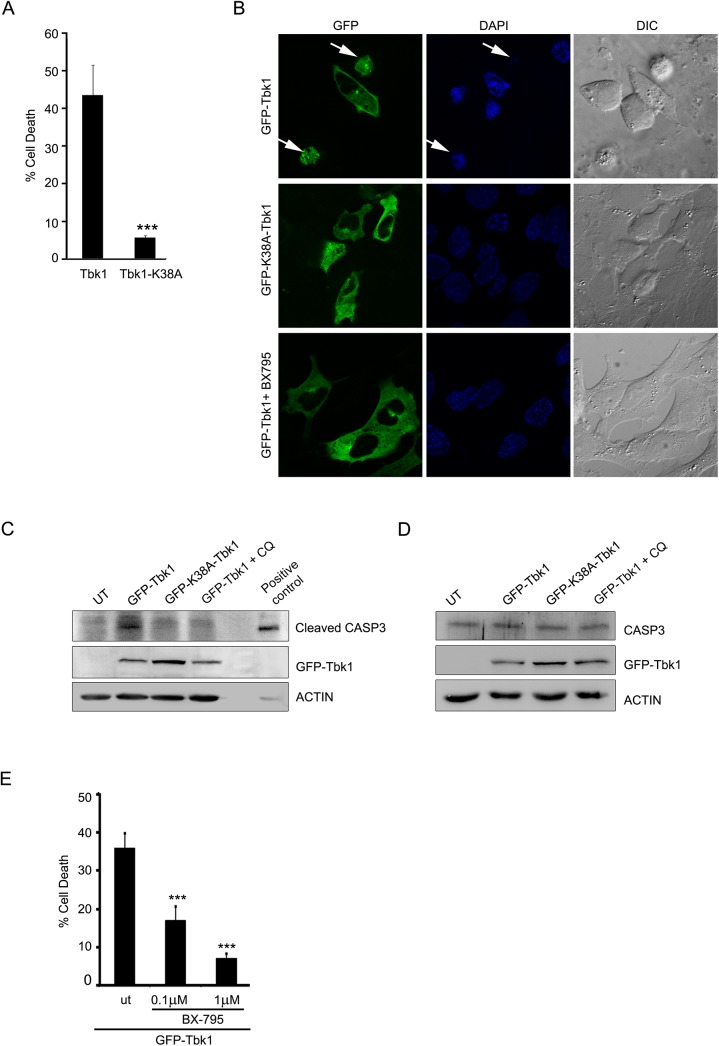
Fig 6. Tbk1 induces cell death in RGC-5 cells dependent on its kinase activity.
(A) Overexpression of Tbk1 induces cell death while catalytically inactive mutant (K38A) does not induce cell death in RGC-5 cells. Data represent quantitation of cell death induced by GFP-Tbk1. n = 6, ***p < 0.001. (B) RGC-5 cells were transfected with GFP-tagged constructs of Tbk1 with or without treatment with BX-795 (1μM) or K38A-Tbk1 mutant. Panels show images captured using 63X objective of Axioplan2 microscope (Zeiss). DAPI and phase panels indicate nuclear and cell morphology respectively. Arrows indicate apoptotic cells. (C) Western blot shows cleavage of caspase 3 upon overexpression of GFP-Tbk1 with or without chloroquine (CQ) treatment for 18 hrs or GFP-K38A-Tbk1 mutant. Actin was used as loading control. Cells treated with 10 ng/ml TNF and 20 μg/ml cyclohexamide for 6 hrs were used as a positive control. (D) Tbk1 did not change expression of caspase 3. Western blots showing uncleaved caspase 3 upon overexpression of GFP-Tbk1 or K38A-Tbk1 mutant in RGC-5 cells. Actin was used as a loading control. (E) Tbk1-induced cell death in RGC-5 cells is dependent on its kinase activity. RGC-5 cells were transfected with GFP-Tbk1 and after 6 hrs, cells were either left untreated (ut) or treated with BX-795 (0.1μM or 1μM) for 18 hrs. Figure shows quantitation of cell death induced by GFP-Tbk1. n = 6, ***p<0.001.