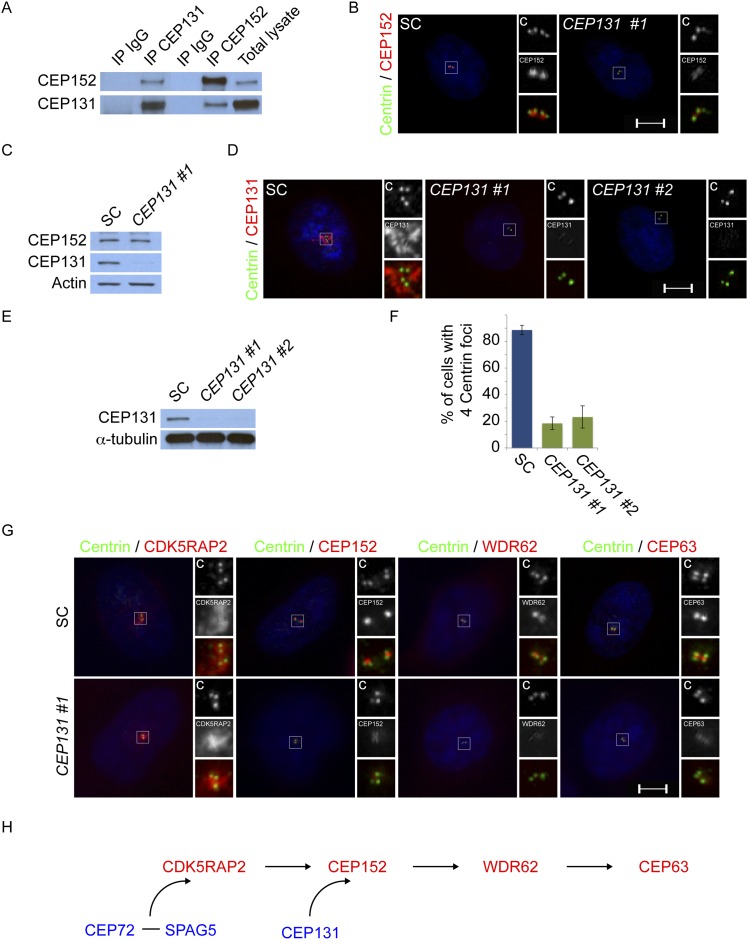
Figure 4. Centriolar satellite component CEP131 interacts with and localizes CEP152 to the centrosome to promote centriole duplication.
(A) HeLa total cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation of CEP131, CEP152 and a negative control. Precipitating proteins were subjected to immunoblotting for CEP131 and CEP152. (B) HeLa cells in S phase transfected with SC or CEP131 #1 siRNA were co-stained for CEP152 (red) and Centrin (‘c’, green). (C) Total cell lysates of SC and CEP131 #1 siRNA transfected HeLa cells were analyzed by immunoblotting with antibodies to CEP131 and CEP152. Actin served as a loading control. (D) HeLa cells in S phase transfected with SC, CEP131 #1, or CEP131 #2 siRNA were co-stained for CEP131 (red) and Centrin (‘c’, green) to visualize centrioles. (E) Total cell lysates of SC, CEP131 #1, CEP131 #2 siRNA transfected HeLa cells were analyzed by immunoblotting for Cep131. α-tubulin served as a loading control. 20 μg of protein lysate was loaded per lane. (F) Quantification of the mean percentage of SC, CEP131 #1, or CEP131 #2 siRNA transfected cells in S phase with four centrioles. (G) SC and CEP131-depleted S phase cells were co-stained with Centrin (‘c’, green), CDK5RAP2 (red), CEP152 (red), WDR62 (red), and CEP63 (red). (H) Schematic indicating that CEP131 is required to localize CEP152, WDR62 and CEP63 to the centrosome. For all quantifications at least 100 cells were counted per experiment (n = 3), p < 0.005 (paired t-test). Scale bars indicate 5 μm for all images.
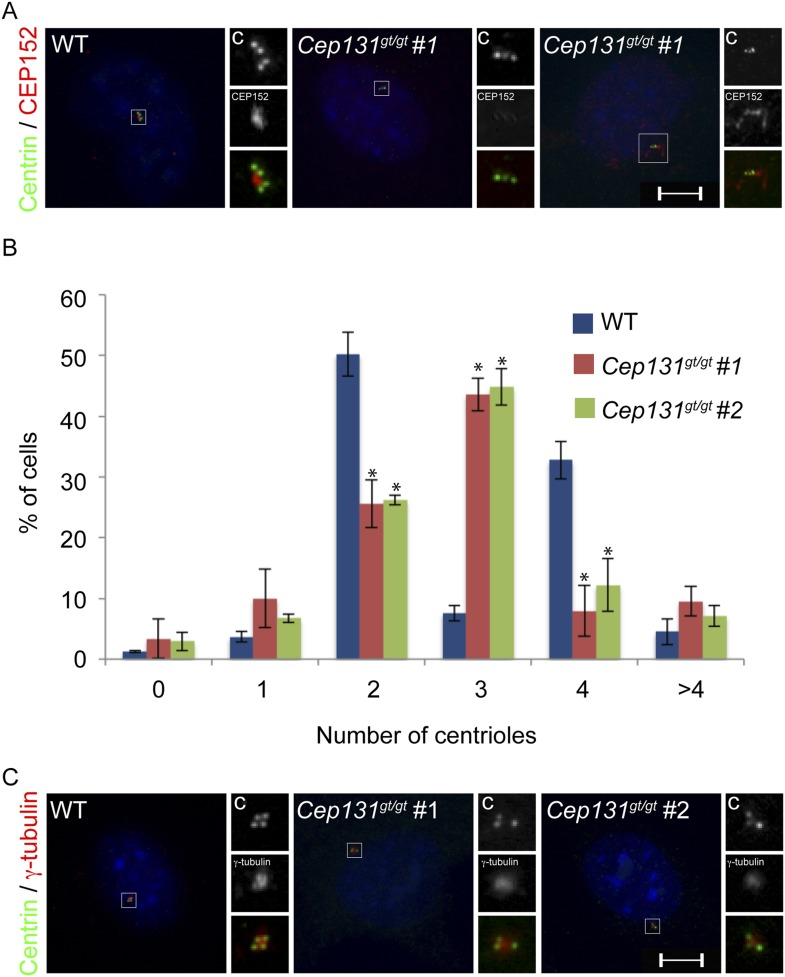
Figure 4—figure supplement 1. Cep131gt/gt MEFs exhibit centriole duplication and centrosome organizational defects.
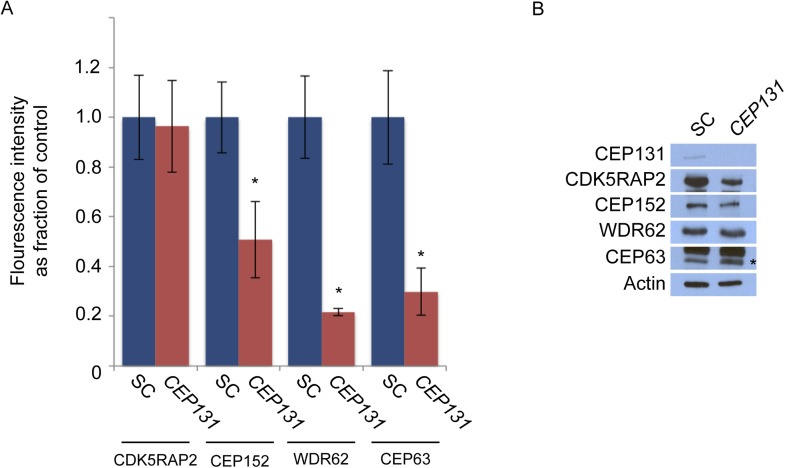
Figure 4—figure supplement 2. CEP131 is required for the centrosomal localization of CEP152, WDR62 and CEP63.
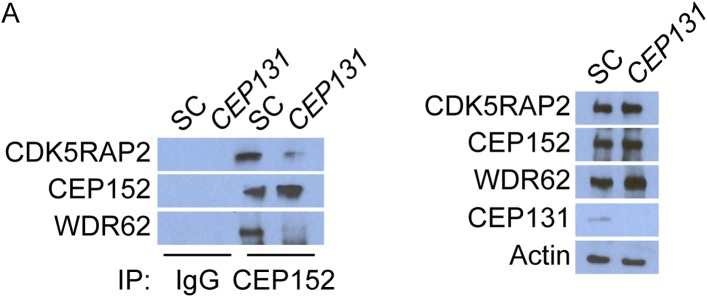
Figure 4—figure supplement 3. CEP152 associates with CDK5RAP2 and WDR62 in a CEP131-dependent manner.