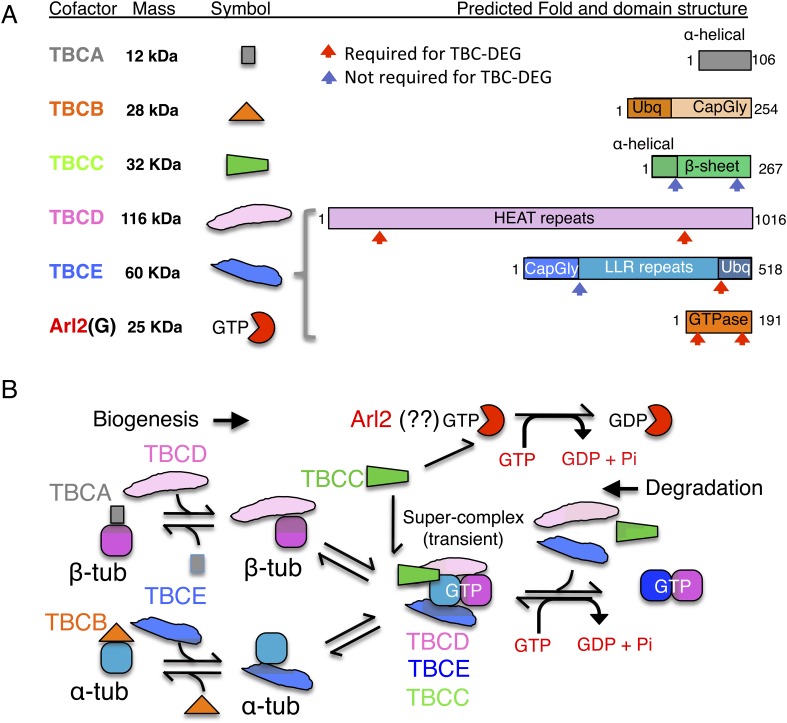
Figure 1. Tubulin cofactors and Arl2 GTPase: domain organization and paradigm for function.
(A) Tubulin cofactors A–E, Arl2 GTPase masses, and domain organization. TBCA and TBCB co-expression is not required for TBC-DEG expression. Red arrowheads mark domains required for forming TBC-DEG complex assembly. Blue arrowheads mark domains not required for TBC-DEG complex assembly. (B) Initial paradigm for tubulin cofactors and Arl2 activities based on previous studies. Each of the molecules is suggested to be monomeric, and only assemble into complexes to drive αβ-tubulin biogenesis or degradation, via interactions regulated by dynamic equilibria. TBCA binds nascent β-tubulin and TBCB binds nascent α-tubulin. TBCA and TBCB are replaced by TBCD and TBCE, respectively. TBCC drives TBCE-α-tubulin and TBCD-β-tubulin to form a supercomplex. GTP hydrolysis in Arl2 is activated by TBCC in a parallel pathway to tubulin assembly. Tubulin biogenesis and degradation intermediate bind and form tubulin dimers, a process that requires Arl2 and tubulin to undergo GTP hydrolysis as an energy source. (Adopted from Lewis et al., 1997.)