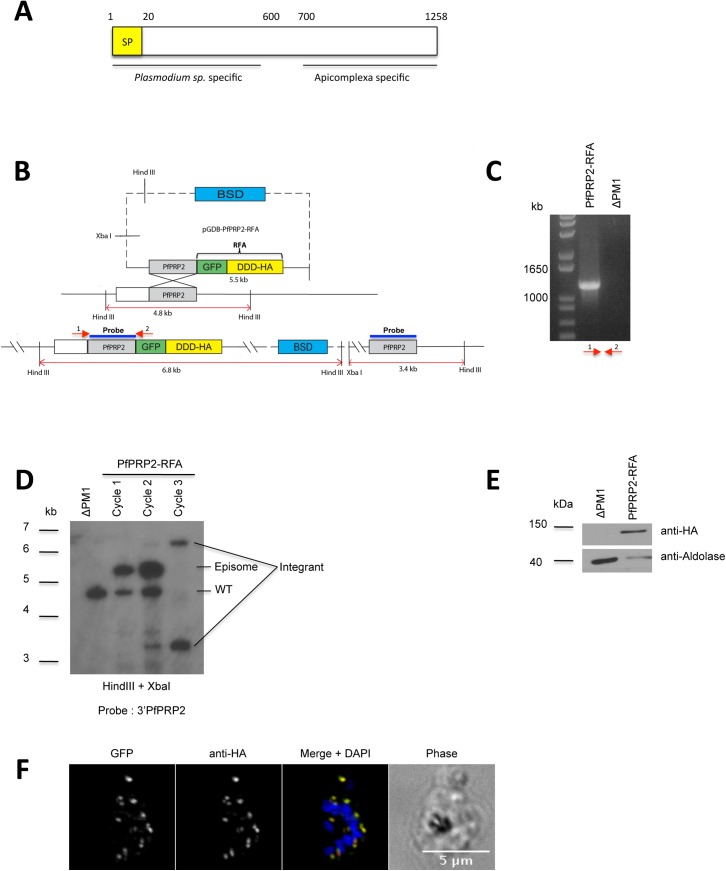
Fig 1. Generation of a PfPRP2-RFA tagged parasite line.
(A) Domain organization of PfPRP2. BLAST analysis reveals that the N-terminus is only present in Plasmodium species whilst the C-terminus is conserved in a number of apicomplexans. The conserved regions were identified using the full length PfPRP2 sequence through protein BLAST at http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi. SP: Signal peptide (B) Schematic of the strategy used to integrate the RFA system at the 3’end of PfPRP2 by single crossover homologous recombination. The expected sizes of digested products for Southern blot are shown. DDD, DHFR degradation domain; BSD, Blasticidin. C) PCR confirming integration of the RFA system at the PfPRP2 endogenous locus. Primers used for amplification are indicated by red arrows. (D) Southern blot showing integration of the RFA cassette at the 3’ of the PfPRP2 locus and the loss of the episomal form of pGDB-PfPRP2-RFA and the wild type PfPRP2 gene after three BSD selection cycles. The 3'PfPRP2 probe consists of nucleotides 2819 to 3774 of PfPRP2. (E) Western blot using a mouse monoclonal anti-HA confirms the expression of PfPRP2-RFA in the tagged line. Anti-Aldolase is used as loading control. (F) IFA using anti-HA (red) or epifluorescence of the GFP (green) on the PfPRP2-RFA tagged line shows an identical punctate pattern. Scale bar represents 5μm. Nuclei of parasites were stain with DAPI (blue).