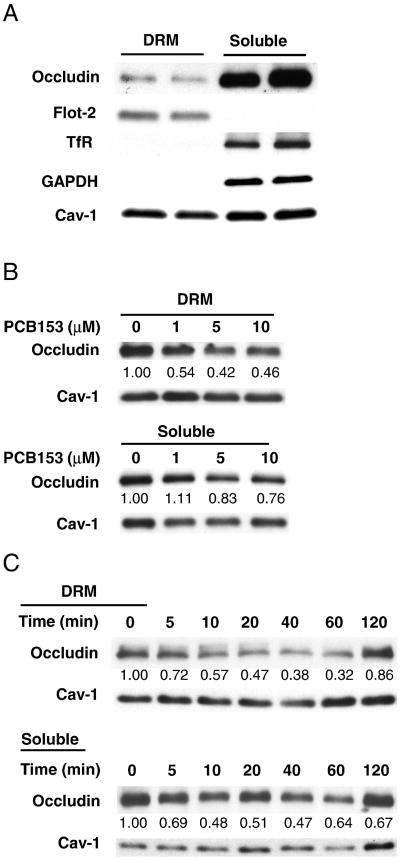
Fig. 1.
PCB153 induces loss of occludin from tight junction assembly. (A) Detergent-resistant membrane fractions (DRM fractions) and detergent-soluble fractions (soluble fractions) of hCMEC/D3 cells were prepared based on solubility in 0.5% NP-40 as described in the Material and methods section. Both fractions were processed for immunoblotting and probed for occludin, flotillin-2 (flot-2, a lipid raft marker), transferrin receptor (TfR, a non-lipid raft transmembrane protein), and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH, a cytosolic protein) and caveolin-1 (Cav-1) expression. (B) hCMEC/D3 cells were incubated with PCB153 at the indicated concentrations for 60 min. The level of occludin in DRM or detergent-soluble fractions was assessed by immunoblotting. Caveolin-1 levels were used as an internal standard. (C) Cells were exposed to 5 μM PCB153 for the indicated time periods, followed by occludin determination in DRM and detergent-soluble fractions. The blots are representative from at least three experiments. The band intensity was determined by the densitometric analysis using Image J program.