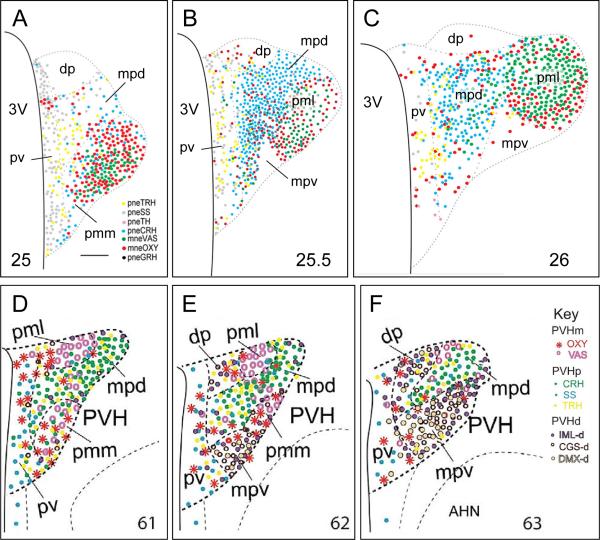
Figure 4.
A – C) Three maps of the rat PVH taken from a reference atlas of neuroendocrine neuron type labeled with antibodies for neuropeptides. The locations of each type of peptidergic neuroendocrine neuron are plotted onto three levels of PVH (designated by the number at the bottom of each panel) from Swanson [2003]. Panels A - C) are adapted from Simmons & Swanson [2009].
D - F) Schematic drawings illustrating the delineations of three levels of the PVH in the mouse brain, which are determined based on distributions of eight neuronal phenotypes in two major neuroendocrine divisions (magnocellular [m] PVHm, including OXY and VAS; and parvicellular [p] PVHp, including CRH, SS, and TRH) and three descending preautonomic populations (PVHd) that project to the intermediolateral column of the spinal cord (IML-d), to the central gray of the spinal cord (CGS-d), and to the dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve (DMX-d). The mouse atlas levels [Dong, 2007] are designated by the number at the bottom of each panel. D - F) are adapted from Biag et al. [2012].
Other abbreviations: 3V, third ventricle; AHN, anterior hypothalamic nucleus; CRH, corticotropin-releasing hormone; dp, ,dorsal parvicellular part of the PVH (descending division); GRH, growth hormone-releasing hormone; mne, magnocellular neuroendocrine; mpd, medial parvicellular part of the PVH, dorsal zone; mpv, medial parvicellular part of the PVH, ventral zone; OXY, oxytocin; pml, posterior magnocellular part of the PVH, lateral zone; pmm, posterior magnocellular part of the PVH, medial zone; pne, parvicellular neuroendocrine; pv, periventricular part of the PVH; SS, somatostatin; TRH, thyrotropin-releasing hormone;VAS, vasopressin.