Fig. 1.
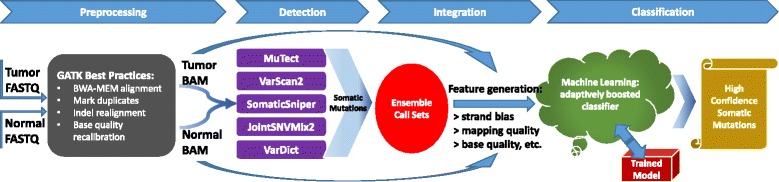
SomaticSeq workflow. The workflow starts with FASTQ files for both the tumor and the matched normal sequencing reads, which are processed using Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) best practices to create two BAM files. The five somatic SNV callers (and three indel callers) are run on the pair of BAM files to generate mutation calls. Their results are merged, and then up to 72 features for each of the combined calls are generated from the BAM files using SAMtools and GATK HaplotypeCaller, as well as outputs from the callers themselves. The ensemble along with the feature set is then provided to the machine-learning model, which is trained with either a separate data set or a portion of these data. After training, the model calculates the probability for each call, yielding a high-confidence somatic mutation call set
