Figure 1.
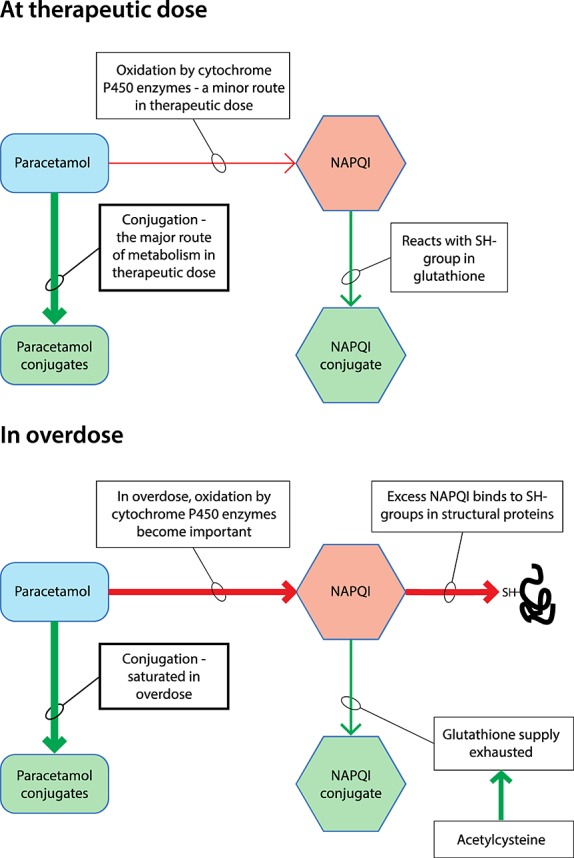
At therapeutic doses conjugation is the major route for paracetamol metabolism. Oxidation of paracetamol by cytochrome P450 is a minor route at therapeutic doses of paracetamol, forming N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) that quickly reacts with glutathione. When an overdose of paracetamol is taken, conjugation becomes saturated and more NAPQI is formed by oxidation. When the glutathione supply is exhausted, NAPQI binds to sulfhydryl (SH-) groups in structural proteins, resulting in cell injury
