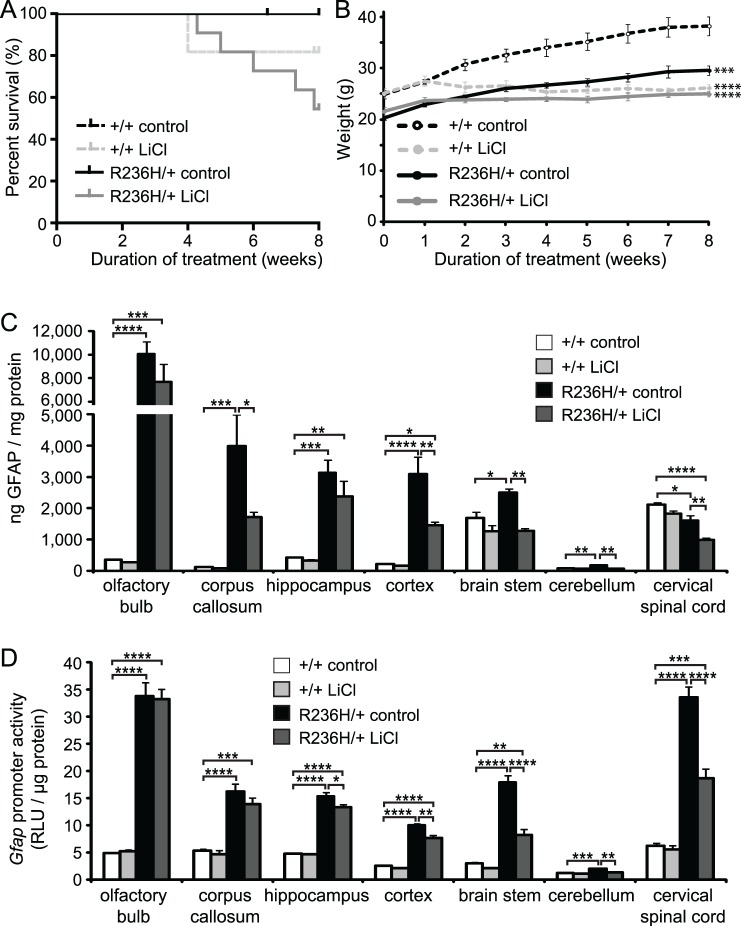
Fig 3. LiCl administered via 0.5% LiCl food pellets for 8 wks decreases GFAP levels in surviving Gfap-R236H/+ mice.
(A) 81.8% (9/11) +/+ mice and 54.5% (6/11) R236H/+ mice survived 8 wks of LiCl treatment. All mice survived control diet treatment. (B) LiCl-treated +/+ and R236H/+ male mice had lower body weights compared with control-treated mice (N = 4–6 cages, 6–11 mice per group). (C) 0.5% LiCl treatment decreased GFAP in corpus callosum, parietal cortex including underlying white matter (cortex), brain stem, cerebellum, and cervical spinal cord of R236H/+ male mice as measured by ELISA (N = 3–4 cages, 4–6 mice per group). (D) 0.5% LiCl decreased Gfap promoter activity in hippocampus, cortex, brain stem, cerebellum, and cervical spinal cord of R236H/+; Gfap-luc mice (N = 3–5 cages, 4–5 mice per group). Error bars are SEM. ****P < 0.0001, ***P < 0.001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. * is versus +/+ control in B.