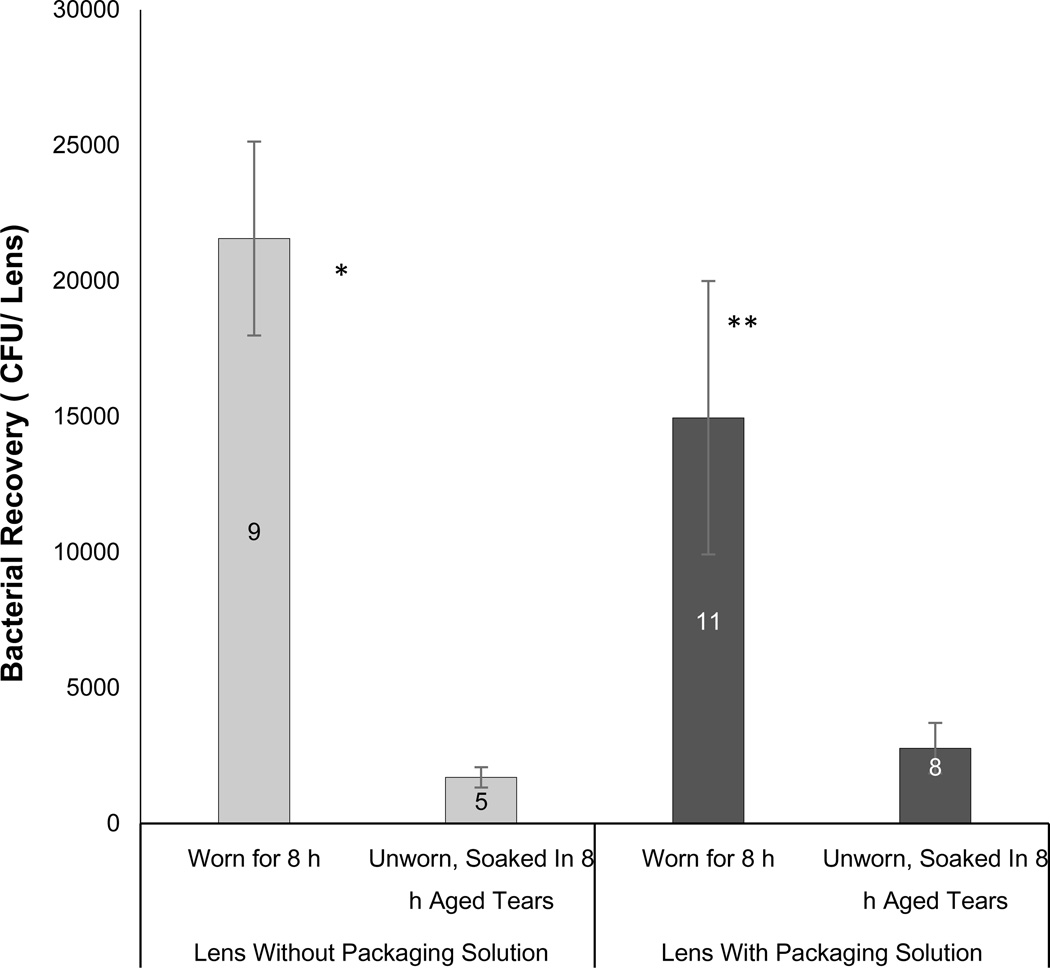
Figure 3.
Comparison of post-lens antimicrobial activity between Omafilcon A lenses worn for 8h versus the same lens type unworn and soaked in human tear fluid that had been previously aged for 8h in vitro. Lenses were inoculated with ~103cfu of P. aeruginosa PAO1 + pJNEO5 and incubated for 3 h before recovery of viable bacteria from lens homogenates. Prior to bacterial exposure, lenses were either worn for 8h, or were unworn and soaked in human tear fluid previously aged for 8h in vitro. Lenses were used directly after removal from original packaging solution (black bars), or after presoaking in sterile saline for 2 days (gray bars). Data show mean (+/− SEM) number of P. aeruginosa recovered per lens after 3h in vitro. Worn lenses were significantly less antimicrobial than unworn lenses soaked in tear fluid for both presoaked lenses (*p = 0.003) and lenses used directly from their packaging solution (**p = 0.004). Numbers on the bars indicate the number of lenses used for each data point.