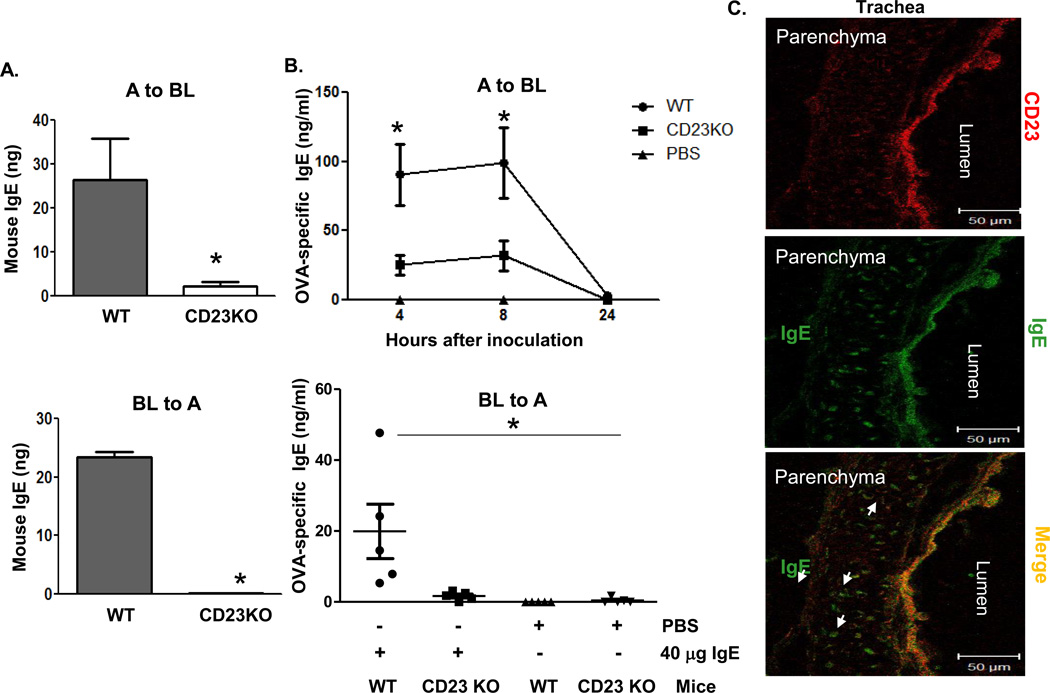
Fig 2. CD23-mediated transcytosis of IgE across mouse epithelial monolayers.
A. Transcytosis of mouse IgE in primary mouse tracheal epithelial cells (TEC). TEC isolated from WT or CD23 KO mice were grown on transwell filters and cells were allowed to become polarized. Mouse IgE was added to the apical (top panel) or basolateral (lower panel) chambers and incubated at 37°C for 2 h. The medium from opposite chamber was collected and IgE concentration was measured by ELISA. A: Apical; BL: Basolateral. *P<0.05.
B. Airway transcytosis of mouse IgE in wild type (WT) or CD23 KO mice. Top Panel: OVA-specific IgE (40 µg) was i.n. inoculated into either WT or CD23 KO mice for 5 min. Sterile PBS was used as a control. Sera were collected at indicated time points. Bottom Panel: OVA-specific IgE (40 µg) or sterile PBS was i.p. inoculated into either WT or CD23 KO mice. BAL fluid was collected 8 h after injection. OVA-specific IgE was measured in the sera and BAL fluid by ELISA. *P<0.05.
C. Colocalization of CD23 and IgE in mouse trachea. Naive mice were anaesthetized with avertin and 20 µg of mouse IgE or PBS was i.n. inoculated. Mice were sacrificed 20 min after treatment, and the trachea was collected and snap frozen in OCT medium and cryosectioned at 5 µm. Frozen tissue sections were fixed and permeabilized with ice-cold acetone and blocked with 10% normal goat serum (NGS). Sections were incubated with rabbit anti-CD23 Ab followed by staining with Alexa Fluor 555-conjugated goat anti-rabbit Ab (red) and FITC-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgE Ab (green). Lung epithelial cells did not stain positive with rabbit anti-IgE Ab. Images were captured using a LSM510 confocal microscope. Samples were visualized under consistent contrast and brightness settings. Arrows indicate IgE Ab transported into the parenchyma.