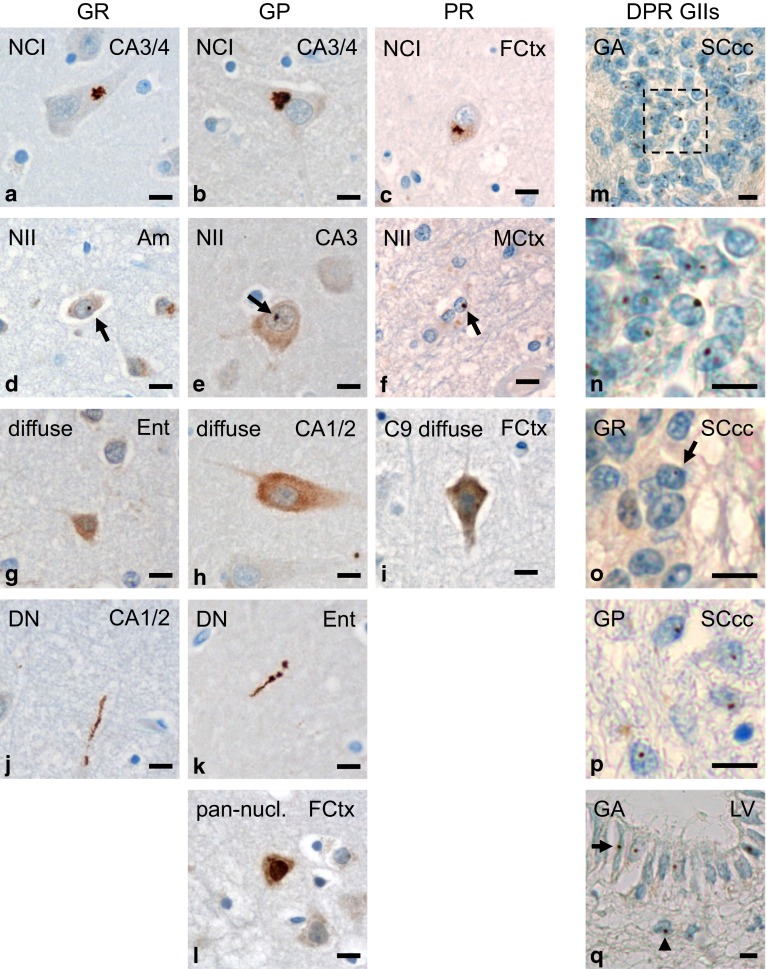
Fig. 4.
Spectrum of DPR pathology in neurons and glial cells of patients with C9orf72 mutation. a–l Immunohistochemistry with novel monoclonal antibodies for poly-GR (clone 7H1), poly-GP (clone 7A5) and poly-PR (clone 32B3) in cases with C9orf72 mutation. Poly-GR, poly-GP and poly-PR mainly form compact characteristic star-like cytoplasmic (a–c) or small round intranuclear inclusions (arrows in d–f) in neurons and show a diffuse granular cytoplasmic staining (g–i). Furthermore there are poly-GR and poly-GP aggregates in dystrophic neurites (j, k); note that dystrophic neurites with poly-PR could not be detected. Solely for poly-GP, a diffuse pan-nuclear staining is also found (l). m–q Immunohistochemistry with indicated DPR antibodies shows glial intranuclear inclusions in C9orf72 cases. In ependymal cells of spinal cord central canal intranuclear inclusions of poly-GA (m, n detail of m), and less frequently of poly-GR (o) and poly-GP (p) are detectable; further glial intranuclear inclusions of poly-GA are present in ependymal (arrow) and subependymal (arrowhead) cells of the lateral ventricle wall at level of accumbens nucleus (q). Scale bars represent 20 µm. Am amygdala, CA cornu ammonis region, DN dystrophic neurite, Ent entorhinal cortex, FCtx frontal cortex, GII glial intranuclear inclusion, MCtx primary motor cortex, LV wall of lateral ventricle, NCI neuronal cytoplasmic inclusion, NII neuronal intranuclear inclusion, SC spinal cord, SCcc spinal cord central canal