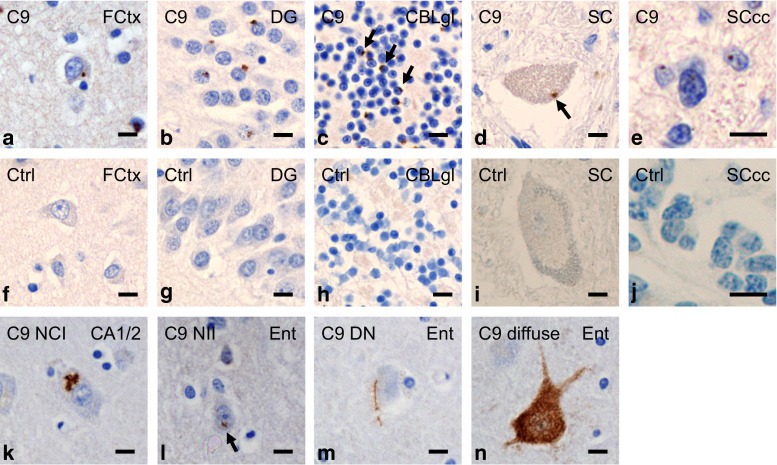
Fig. 7.
Spectrum of Unc119 pathology in cases with C9orf72 mutation resembles poly-GA pathology. Immunohistochemistry with a polyclonal rabbit antibody against Unc119. In C9orf72 mutation cases, numerous Unc119 inclusions are seen in neurons of various brain areas (a–c), rarely in motoneurons of spinal cord (d) and in ependymal cells of spinal cord central canal (e); examples of cytoplasmic inclusions are marked by arrows. (f–j) Corresponding areas of control cases do not contain such inclusions and the proteinase K pretreatment removes all soluble Unc119 staining in cases and controls. (k–n) The types of Unc119 aggregates are similar to those of DPR proteins. There are often star-like neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions (NCI) (k), neuronal intranuclear inclusions (NII, pointed by arrow in l), compact aggregates in dystrophic neurites (DN) (m) and diffuse granular cytoplasmic aggregates in neurons (n). Scale bars represent 20 µm. C9 case with C9orf72 mutation, CA1/2 cornu ammonis fields 1/2, CBLgl granular cell layer of cerebellum, Ctrl control case, DG dentate gyrus, Ent entorhinal cortex, FCtx frontal cortex, SC spinal cord, SCcc spinal cord central canal