Figure 2.
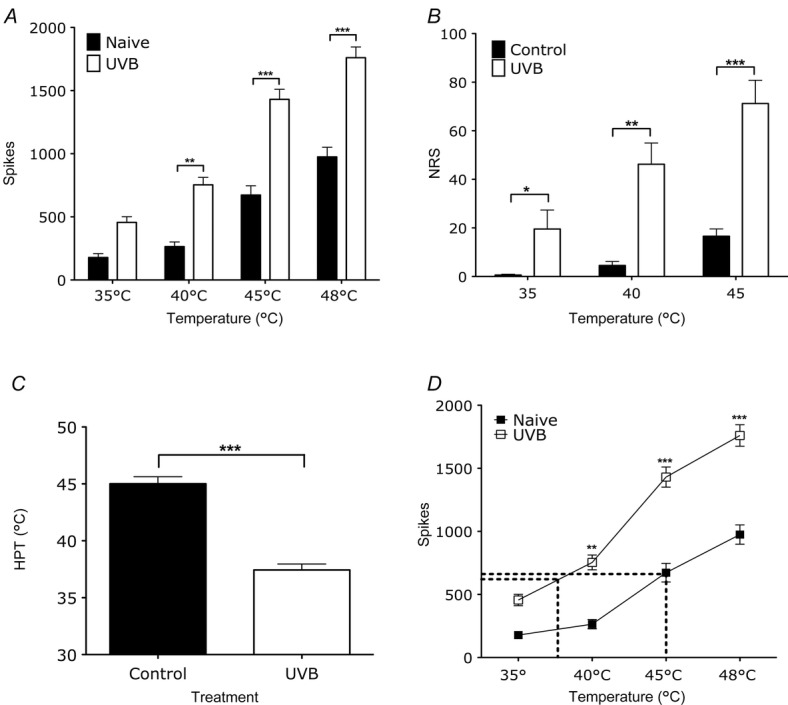
UVB irradiation enhances thermally evoked firing of rat WDR neurones that corresponds to enhanced sensory function humans
A, evoked firing of rat WDR neurones in the deep dorsal horn by low- and high-threshold thermal stimulation is enhanced in UVB rats compared to naive rats (two-way ANOVA, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). B, human pain ratings to low- and high-threshold thermal stimulation is enhanced following UVB irradiation (paired t test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). C, human pain thresholds are significantly reduced following UVB irradiation (paired t test, ***P < 0.001). D, correlating thermally evoked firing of WDR neurones in naive and UVB rats with human pain thresholds in the control (37.4°C) and in the UVB condition (40°C) (two-way ANOVA, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001).
