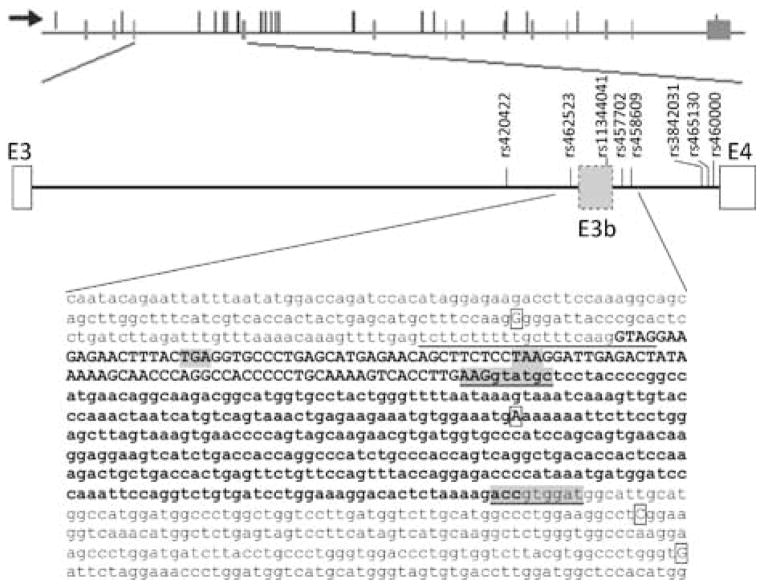
Figure 1.
Predicted exon E3b and location of significant SNPs. Top panel: SLC6A3 transcription unit. The horizontal line represents the gene, with exons as vertical bars crossing the line. Nominally significant SNPs are shown as thin vertical lines that do not cross the horizontal lines. The arrow indicates the orientation of transcription. Middle panel: Predicted cassette exon E3b. Diagram of genomic region from exon 3 (E3) through exon 4 (E4) of SLC6A3. Vertical lines with labels indicate schizophrenia-associated SNPs or SNPs in significant LD with SZ-associated SNPs in the PITT/Bulgarian samples. The long form of E3b (using the downstream 5′ splice site underlined in the bottom panel) is represented. Bottom panel: Sequence of E3b and flanking intron regions. The predicted 3′ splice site region is underlined. This contains two potential intron-terminating trinucleotides in tandem (aagGTAG). The two strongest 5′ splice site motifs are underlined and highlighted in gray. The exon sequence between the first 3′ splice site (aag/G) and the first 5′ splice site (AAG/gtatgc) is in bold uppercase. The exon sequence between the two 5′ splice sites is in bold lower case. The first in-frame stop codons within E3b are highlighted in gray: TAA is encountered if the upstream 3′ splice site is used, TGA is encountered if the downstream 3′ splice site is used. PITT/Bulgarian Schizophrenia-associated SNP positions are boxed; the risk-associated allele is shown in each case.