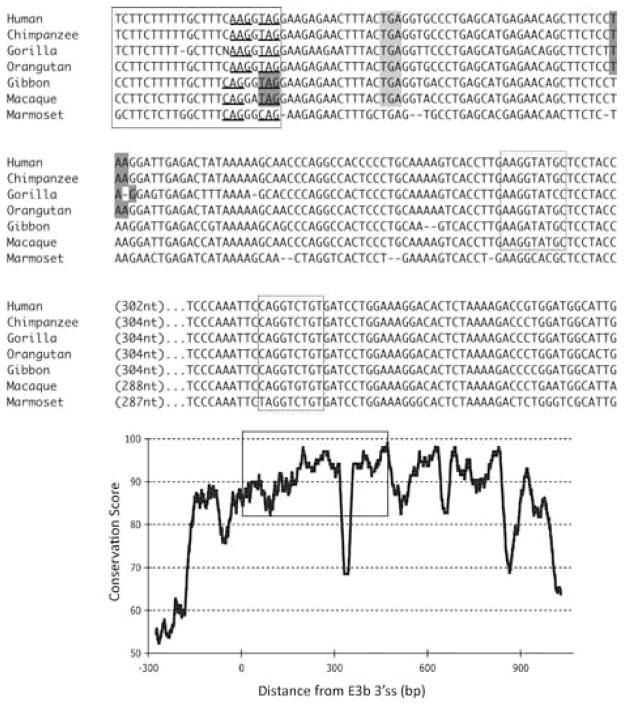
Figure 2.
Conservation of E3b features among simian primates. Top panel: Multiple sequence alignment generated with Clustal 2.0.5. Solid outline: predicted 3′ splice sites. The tandem intron-terminating trinucleotide motifs are underlined. Dashed outline: predicted 5′ splice sites. Light gray: first in-frame stop codon when the downstream 3′ splice site is used. In Marmoset, the first in-frame stop codon lies within the omitted sequence. Dark gray: first in-frame stop codon when the upstream 3′ splice site is used. Bottom panel: Conservation plot for the E3b region. Conservation scores were calculated using the Clustal X software for every column of the multiple sequence alignment that contained a non-gap symbol in human. The graph was smoothed by plotting the moving averages of the scores for every 30 columns. The rectangle indicates the region from the upstream 3′ss of E3b to the downstream 5′ splice site highlighted in the top panel.