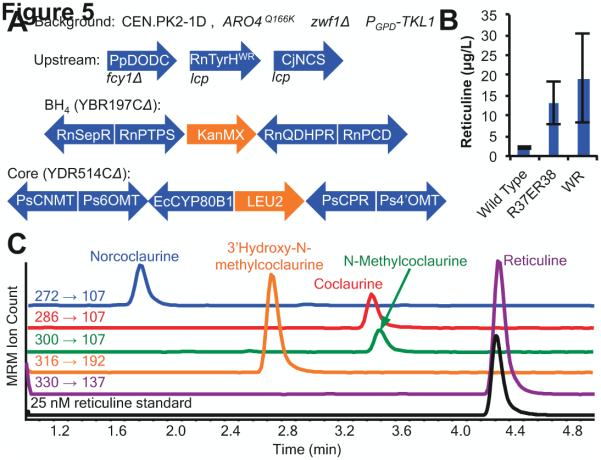
Figure 5.
De novo production of reticuline in engineered yeast. (A) Schematic depicting heterologous expression constructs in final strain design. Blue indicates heterologous enzymes, orange indicates selection marker. lcp, low-copy plasmid. (B) Reticuline production as a function of RnTyrH mutant. CSY1052 strains harboring plasmids with RnTyrH (pCS3231), RnTyrHR37ER38E (pCS3235), or RnTyrHWR (pCS3238) and CjNCS (pCS3241) were grown in selective media lacking tyrosine and supplemented with 2 mM ascorbic acid for 96 hours before analysis. Data is reported as the mean ± s.d. of at least 3 independent experiments. (C) LC-MS/MS MRM analysis of pathway intermediates from norcoclaurine to reticuline in CSY1052 expressing RnTyrHWR (pCS3228) and CjNCS (pCS3241). Cultures were grown in selective media lacking tyrosine and supplemented with 2 mM ascorbic acid for 96 hours before analysis. Reticuline standard (25 nM) shown in black.