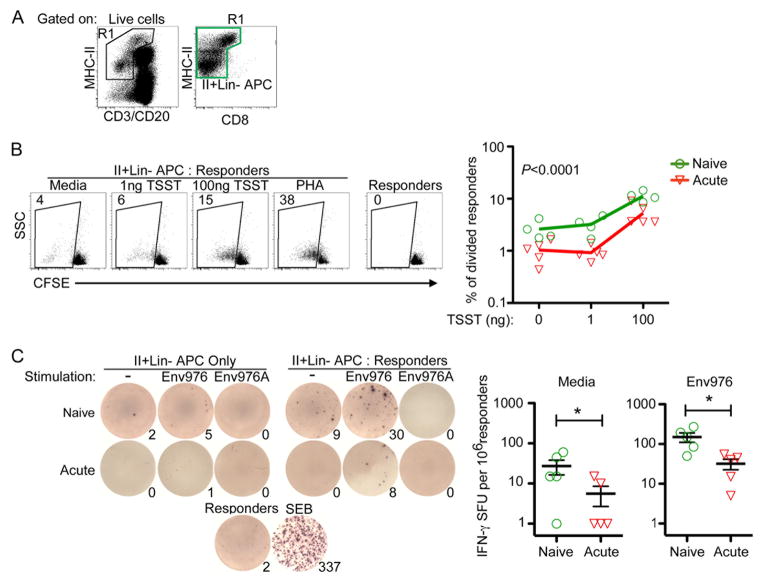
Fig. 1. Enriched mononuclear phagocytes from SIV infected lymph nodes are impaired at stimulating allogeneic CD4 T cells.
(A) Gating strategy to generate enriched mononuclear phagocytes through live-cell sorting. The green gate represents the MHC-II+Lin− population that was added to each co-culture assay. The gate encompasses MHC-IIbright cells that have high autofluorescence. (B) (Left) MHC-II+Lin- mononuclear phagocytes from naïve or acutely-infected lymph nodes were incubated with CFSE-labeled allogeneic CD4 T cells with varying concentrations of TSST or PHA. Numbers represent the percentage of T cells that have diluted their CFSE intensity. (Right) Graphical representation of T cell division induced by enriched mononuclear phagocytes isolated from naïve or acutely infected lymph nodes. Each symbol represents an individual animal. An ANOVA was performed and subsequent multiple comparisons tests revealed a P-value of <0.0001. (C) (Left) MHC-II+Lin- cells from naïve or acutely-infected lymph nodes were either stimulated with Env976 or not and co-cultured with 200,000 allogeneic CD4 T cells directly in an anti-IFN-γ coated ELISPOT plate. Numbers represent IFN-γ spot-forming units (SFU) per 1 million responder CD4 T cells. (Right) Graphical representation of IFN-γ SFU by enriched mononuclear phagocytes isolated from naïve or acutely infected lymph nodes. Each symbol represents an individual animal. Repeated measures ANOVA and multiple comparisons tests were performed and each significant relationship is shown with capped bars. *P=0.03