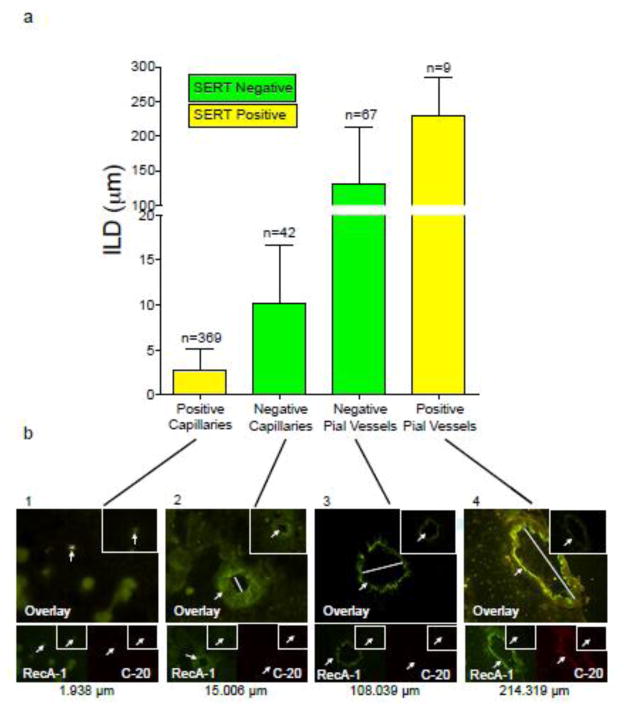
Figure 2.
Figure 2a. SERT colocalization with RecA-1 and intraluminal diameter of rat brain blood vessels.
The graph shows SERT-positive and SERT-negative rat brain blood vessel sizes, with intraluminal diameter (ILD μm) on the y-axis and capillaries and pial vessels on the x-axis. Bars represent mean ILD ± SEM. Yellow indicates SERT-positive, colocalized vessels. Green indicates SERT-negative vessels. All vessels quantified have RecA-1 present. The number of vessels in each category and the range are noted above each bar.
Figure 2b. SERT colocalization with RecA-1 and intraluminal diameter of rat brain blood vessels.
Each of the four panels corresponds to a category of the graph in figure 2a, demonstrating the appearance of vessels from each category. The top panel is an overlay of the FITC and TRITC channels. In the bottom left of each panel RecA-1 (an endothelial cell marker) is shown on the FITC channel (green) while in the bottom right of each panel, ST C-20 (a SERT marker) is shown on the TRITC channel (red). In the upper right-hand corner of each image the negative control (without primary but with secondary present) is shown. Arrows indicate the vessel in each image and a bar is shown across the intraluminal diameter of the overlay images to indicate the size of each vessel. Magnification across the four panels is 100×, 100×, 40×, 40× from left to right.