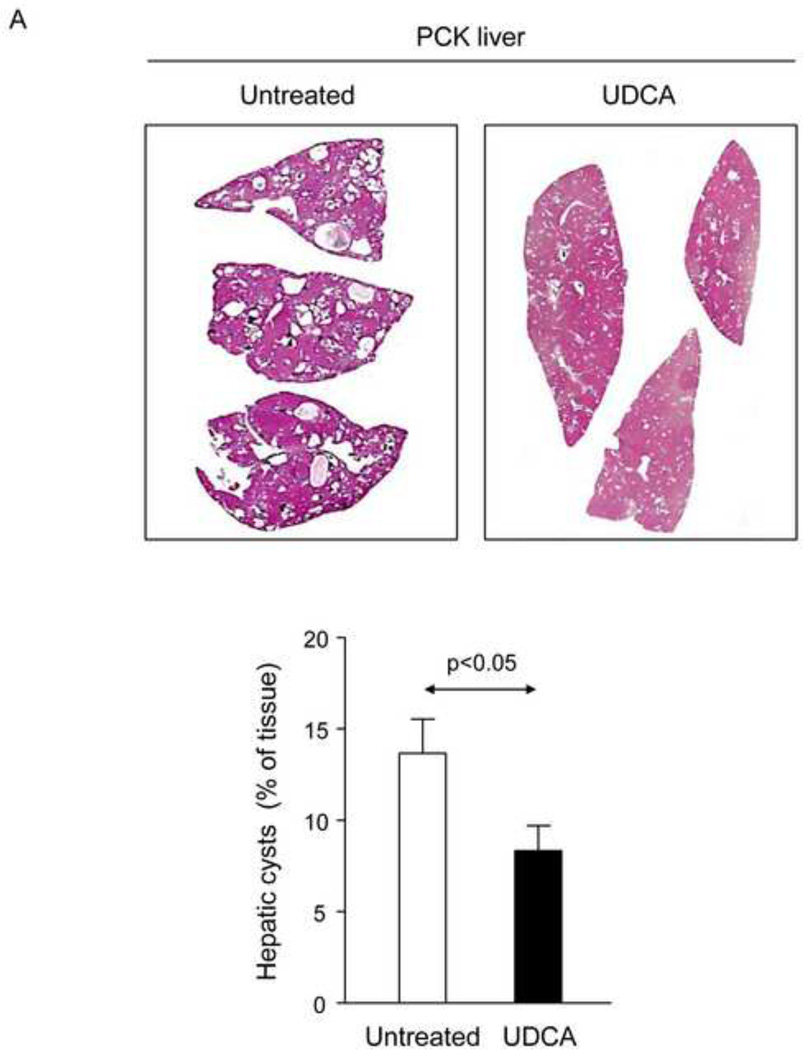
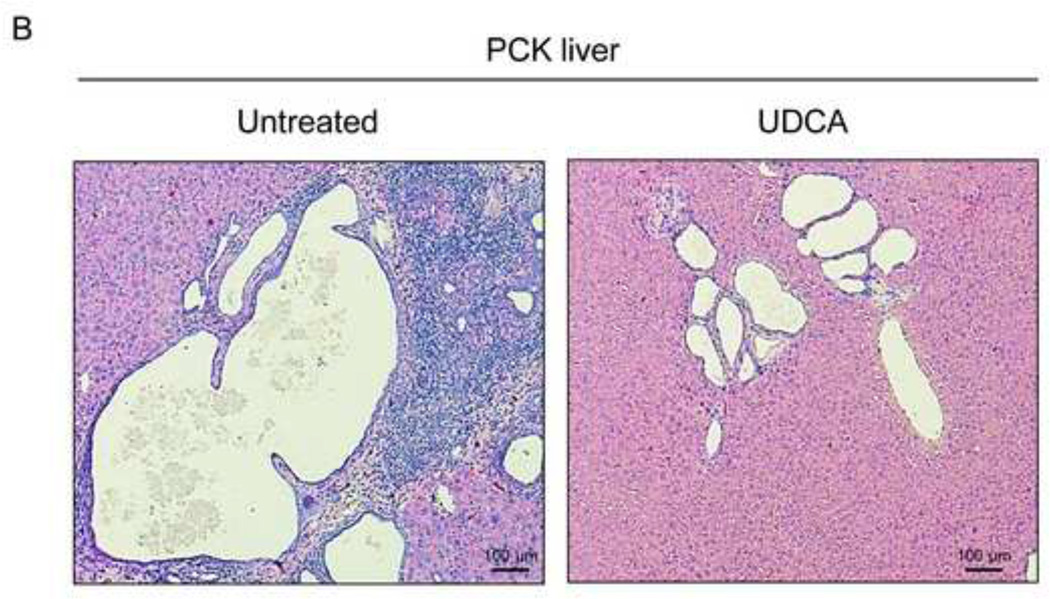
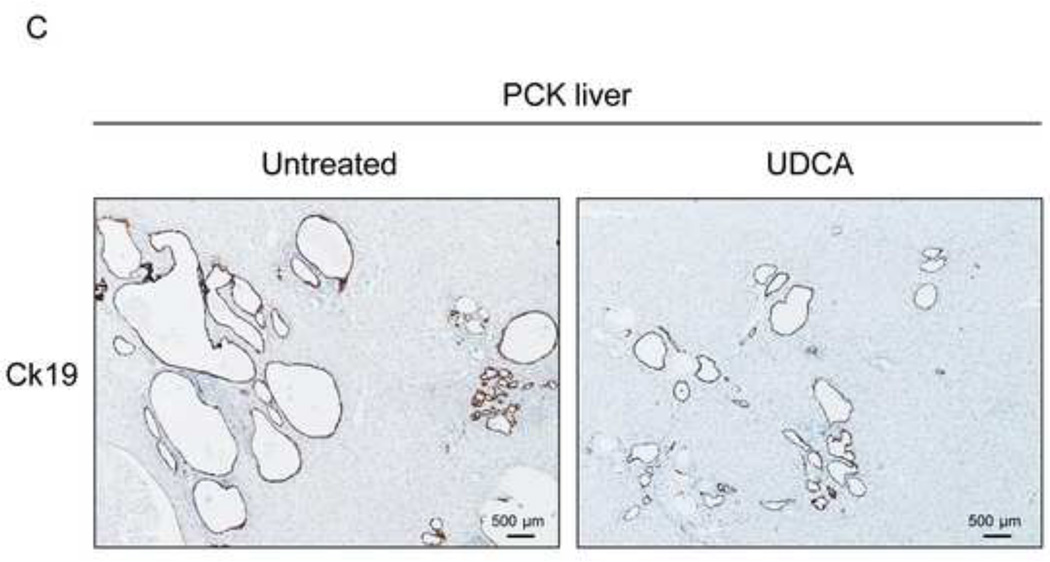
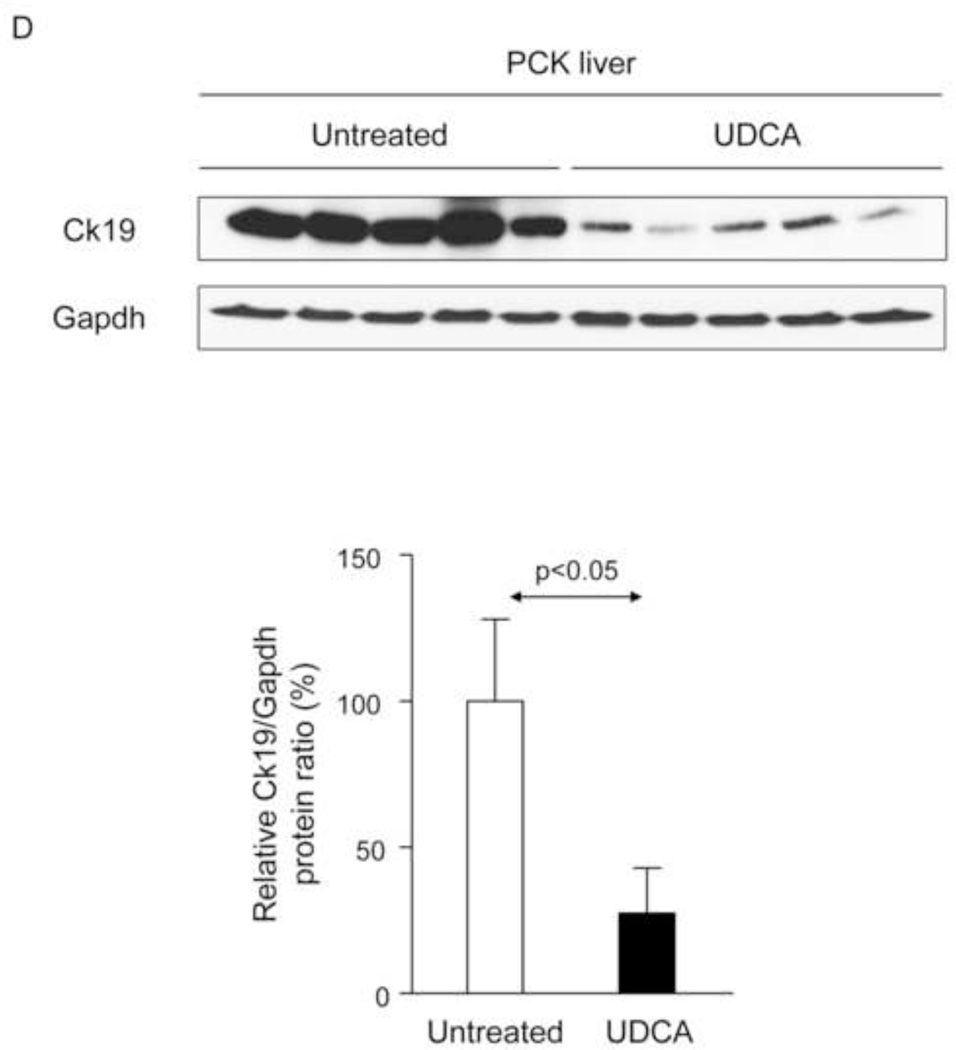
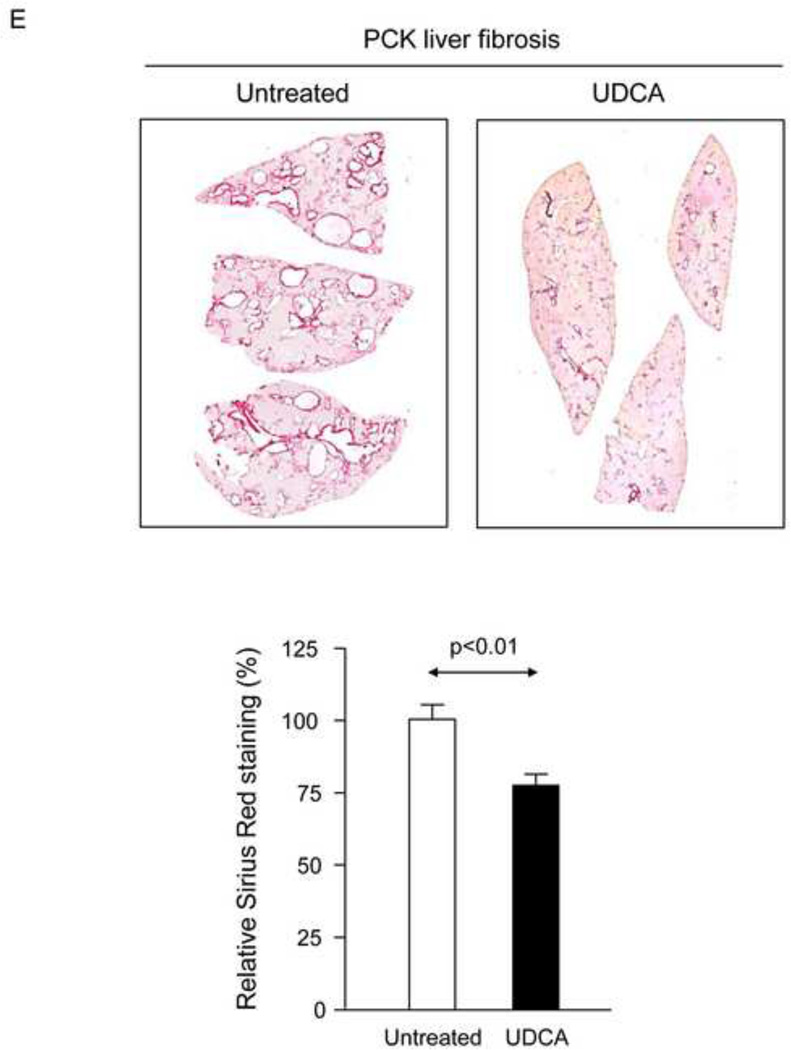
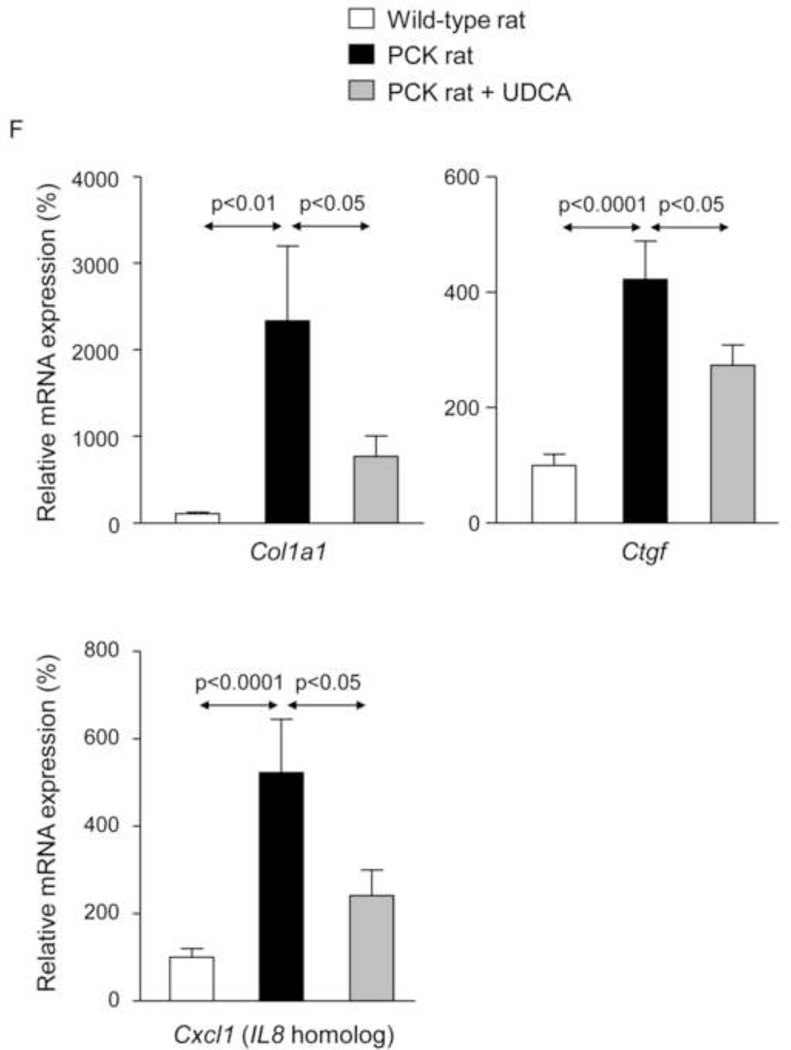
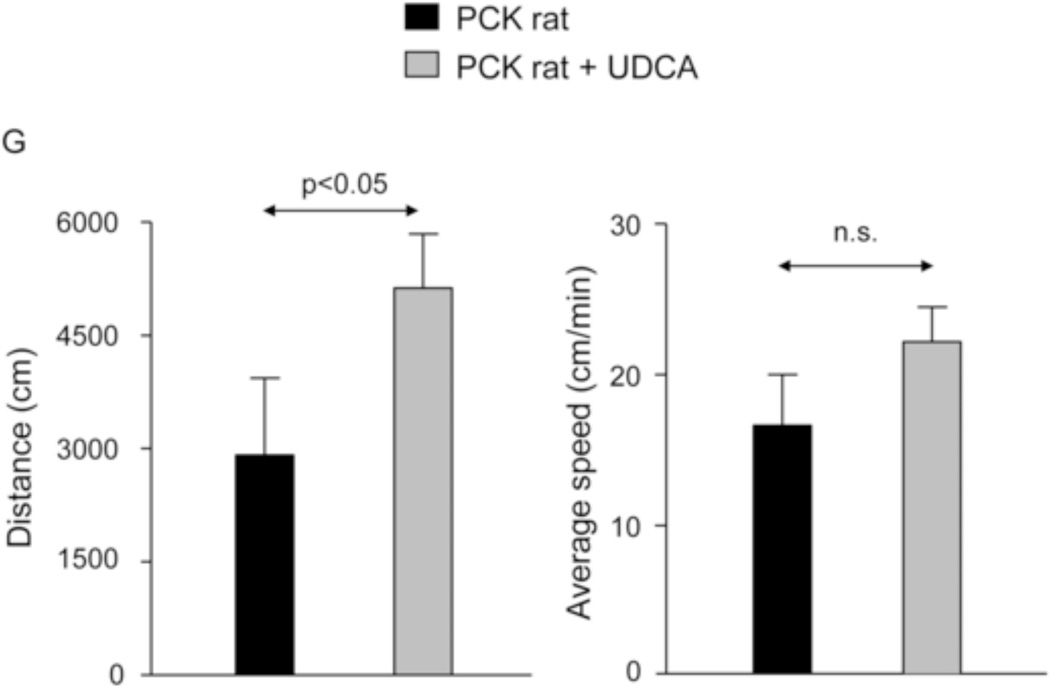
Figure 1.
Treatment of PCK rats with UDCA halts hepatic cystogenesis and fibrosis, and improves their motor behaviour. (A and B) Representative images (hematoxylineosin staining; 5× magnification in Fig. 1A) and bar graph showing hepatic cysts in untreated and UDCA-treated PCK rats. (C and D) Hepatic expression of the cholangiocyte-marker Ck19 at protein level. Representative images of Ck19 immunohistochemistry (C) and western blots (D) of 5 representative untreated or UDCA-treated PCK rats. Bar graph shows Ck19 quantification (n=10 and n=9 in PCK and PCK+UDCA groups, respectively). (E) Representative images (Sirius Red staining; 5× magnification) and bar graph showing the hepatic collagen deposition in untreated and UDCA-treated PCK rats. (F) Expression levels (mRNA) of pro-fibrotic (Col1a1 and Ctgf) and pro-inflammatory (Cxcl1) genes in liver of wild-type and PCK (untreated and UDCA-treated) rats. (G) Open field test (distance and average speed) in untreated and UDCA-treated PCK rats.
N=12 in wild-type (untreated) and n=10 in PCK (untreated and UDCA-treated) groups unless specified.