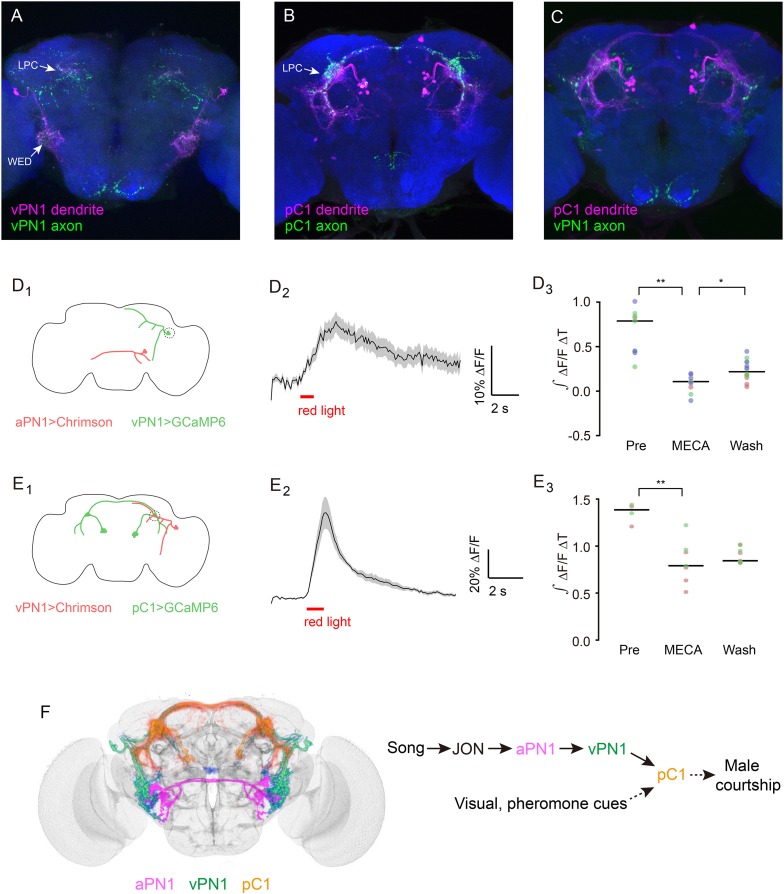
Figure 8. Directionality and functional connectivity of the auditory pathway.
(A–C) Labeling of dendrites and axons by expression of the dendritic marker DenMark (magenta) and axonal marker Syt::GFP (green) in (A) vPN1 neurons (labeled with split GAL4 driver R72E10-GAL4AD ∩ VT009665-GAL4DBD) and (B) pC1 neurons (labeled with split GAL4 driver R71G01-GAL4AD ∩ R15A01-GAL4DBD). (C) Co-registration of vPN1 axons (green) and pC1 dendrites (magenta) onto a standard brain. (D) Activation of aPN1 neurons induced calcium responses in vPN1 neurons. (D1) CsChrimson was expressed in aPN1 neurons with 59C10-LexA, while GCaMP6 was expressed in vPN1 neurons with R72E10-GAL4. Dashed circle indicates the location of the recording site. (D2) aPN1 CsChrimson-mediated activation induced calcium responses in vPN1 neurons. Black line indicates mean while gray envelope indicates SEM. n = 46 from 6 flies. (D3) This effect is suppressed by the acetylcholine receptor antagonist mecamylamine (**p < 0.001, Student's t-test), and partially restored by washing out the antagonist (*p < 0.01, Student's t-test). Dots with the same color represent experiments performed on the same individual. Black lines indicate mean values. n = 9–14 (depending on the drug condition) from 3 flies. (E) Activation of vPN1 neurons induced pC1 calcium responses. (E1) CsChrimson was expressed in vPN1 neurons with a vPN1 split-GAL4 driver while GCaMP6 was expressed in pC1 neurons with dsxLexA. Dashed circle indicates the location of the recording site. (E2) pC1 neurons respond to CsChrimson activation of vPN1 neurons. Black line indicates mean while gray envelope indicates SEM. n = 13 from 3 flies. (E3) Mecamylamine causes a mild reduction in the pC1 responses (**p < 0.001, Student's t-test). Black lines indicate mean values. n = 4–9 from 2 flies. (F) Left panel shows co-registration of aPN1 (magenta), vPN1 (green), and pC1 (yellow) neurons onto a standard brain. The anatomical overlap between them suggests a potentially interconnected circuit mediating courtship song detection in the male brain. We propose that courtship song is relayed through aPN1 and vPN1 neurons to pC1 neurons, and that the pC1 neurons integrate song signals with other sensory cues to initiate courtship.