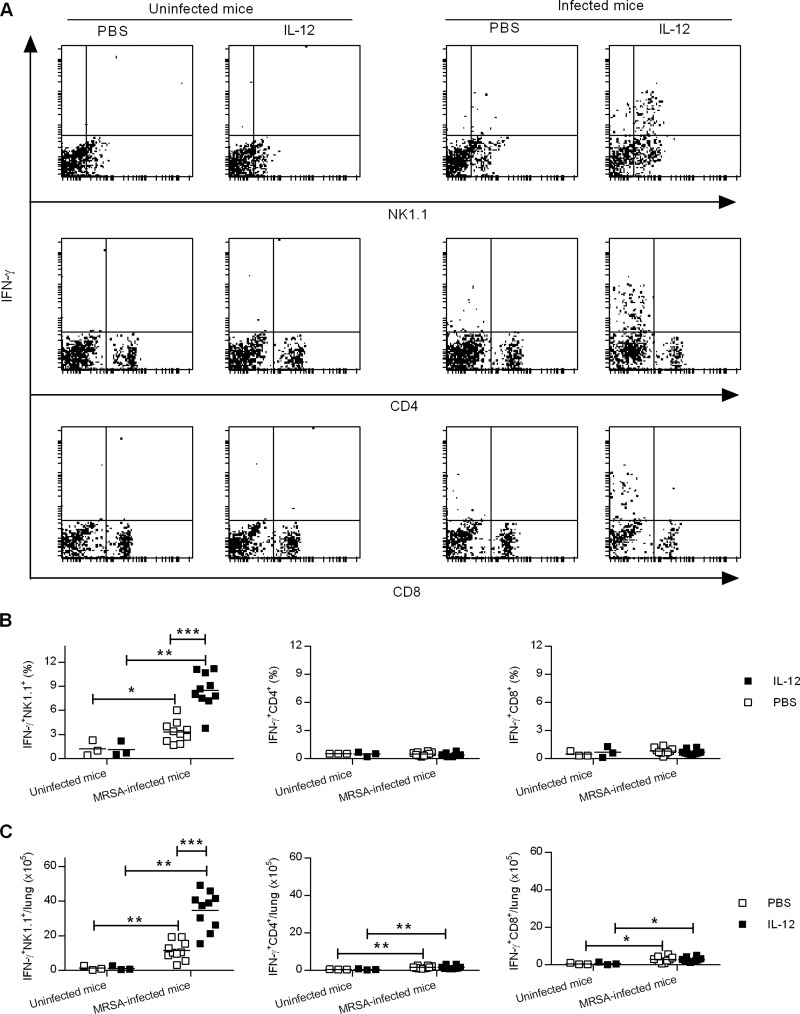
FIG 4.
Intranasal IL-12 treatment induces IFN-γ production by NK cells. WT mice were treated i.n. with either 1 μg of IL-12 or PBS vehicle 24 h before infection with 1 × 108 CFU of MRSA. Lung cells from uninfected mice and mice infected 24 h earlier were isolated and restimulated in vitro with MRSA for 2 h. They were then stained for surface NK1.1, CD4, and CD8 and for cytoplasmic IFN-γ, followed by flow cytometry analysis. (A) Representative dot plots from each experimental group. (B and C) Percentages (B) and numbers (C) of IFN-γ+ NK1.1+, IFN-γ+ CD4+, and IFN-γ+ CD8+ lung cells. Each symbol represents an individual mouse, and the line indicates the mean. The data were pooled from two independent experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by using the Mann-Whitney U test. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001.