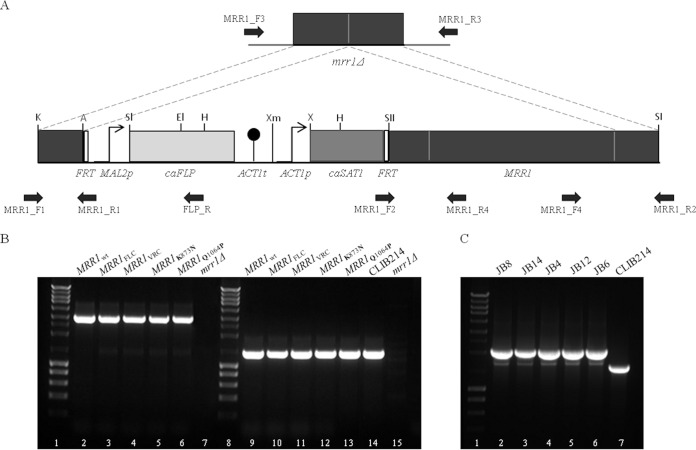
FIG 1.
Genomic integration of the MRR1 transcription factor gene variants in the C. parapsilosis homozygous disruptant mrr1Δ strain. (A) MRR1 complementation cassettes were constructed using the SAT1 flipper cassette (20) and primers MRR1_F1, MRR1_R1, MRR1_F2, and MRR1_R2 (Table 1). MRR1wt, MRRFLC (containing mutation G1747A), MRRVRC (containing mutations A2619C and A3191C), MRR1K873N (containing mutation A2619C), and MRR1Q1064P (containing mutation A3191C) genes were integrated in the C. parapsilosis mrr1Δ double mutant, generating the JB8, JB14, JB4, JB12, and JB6 strains, respectively. Each mutation in MRRVRC was independently silenced by site-directed mutagenesis (Table 1) to originate MRR1K873N and MRR1Q1064P. (B) Complementation cassettes were integrated at the MRR1 native genomic locus and confirmed by PCR using the following pairs of primers: (i) MRR1_F3 and FLP_R, which amplified a 3-kb fragment (lanes 2 to 6; absent in lane 7), and (ii) MRR1_F4 and MRR1_R3, resulting in a 1.3-kb PCR product (lanes 9 to 13). Lanes 14 and 15 show a 1.3-kb fragment present in CLIB214 and absent in the mrr1Δ strain, respectively. Lanes 1 and 8 represent the molecular size marker (NZYDNA Ladder III). (C) Confirmation of the successful recycling of the MRR1 complementation cassettes by PCR using primers MRR1_F3 and MRR1_R4, resulting in the amplification of a 2.1-kb fragment (lanes 2 to 6), CLIB214 was used as control amplifying a 1.7-kb fragment (lane 7). The discrepancy between size fragments amplified in the transformants and the one amplified in CLIB214 is due to the presence of two promoters regions upstream of the MRR1 gene in the transformants compared with only one in the CLIB214 strain. Lane 1 represents the molecular size marker (NZYDNA Ladder III).