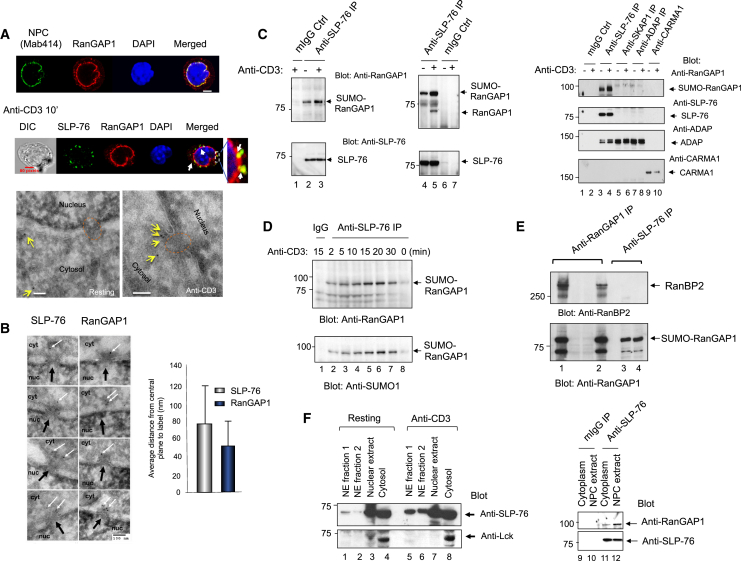
Figure 1.
SLP-76 Localizes at the Cytoplasmic Face of the Nuclear Pore Complex and Interacts with SUMO-RanGAP1
(A) Confocal images of mouse DC27.10 T cells stained with Mab414-Alexa Fluor 488, anti-RanGAP1-Alexa Fluor 633, anti-SLP-76-Alexa Fluor 488 and DAPI (upper and middle panel) (scale bar, 5 μm). TEM images of gold-labeled anti-SLP-76 (yellow arrows) on the cytoplasmic face of the NPC (red dashed circle) (n = 3).
(B) TEM images of gold-labeled anti-SLP-76 and anti-RanGAP1 (white arrows) relative to the NPC (black arrows) upon anti-CD3 stimulation (left). Histogram shows distance of SLP-76 and RanGAP1 from central plane of NPC (right).
(C) Anti-SLP-76 coprecipitated RanGAP1. Resting or anti-CD3 activated DC27.10 T cells (left) or human peripheral blood lymphocytes (middle). Precipitation followed by blotting with anti-RanGAP1 (upper) or anti-SLP-76 (lower) (n = 4). (Right panel) RanGAP1 does not interact with immune adaptors SKAP1, ADAP, or CARMA1 (n = 3).
(D) Time course of RanGAP1 binding to SLP-76 upon anti-CD3 ligation. Blotted with anti-RanGAP1 (upper panel) or anti-SUMO1 (lower) (n = 3).
(E) Anti-SLP-76 does not coprecipitate RanBP2 from anti-CD3-stimulated Jurkat T cells. Blotted with anti-RanBP2 (upper panel) or anti-RanGAP1 (lower). Also see Figure S1.
(F) Anti-CD3 increases SLP-76 recruitment to the NPC. Mouse DC27.10 T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 followed by subcellular fractionation and blotted with anti-SLP-76 (left upper) or anti-lck (left lower). Anti-SLP-76 coprecipitates from NE fraction. Blotted with anti-RanGAP1 (right upper) and anti-SLP-76 (right lower) (n = 4).