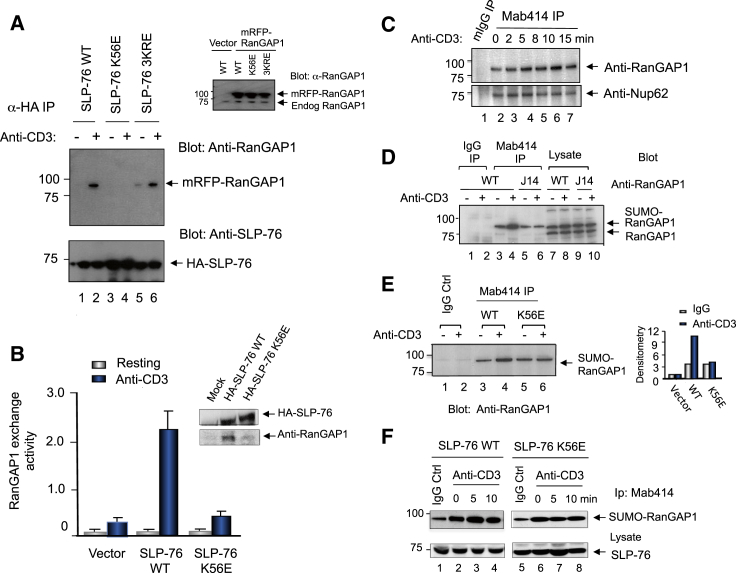
Figure 2.
RanGAP1 Binds to SLP-76 Lysine 56 and Regulates RanGAP1 Binding to NPC
(A) RanGAP1 binds to lysine 56 in the SLP-76 N-terminal domain. SLP-76-deficient J14 T cells cotransfected with HA-tagged SLP-76 or mutants and mRFP-RanGAP1 (n = 3).
(B) Anti-CD3 increases RanGAP1 exchange activity that is lost with K56E. (Upper inset) Blot for HA-SLP-76 wild-type and K56E expression. Data are represented as mean ± SE of a representative experiment (n = 3). Also see Figure S2.
(C) Anti-CD3 ligation increases SUMO-RanGAP1 coprecipitated with anti-NPC Mab414. Cell lysates from DC27.10 T cells were stimulated with anti-CD3 for 15 min, followed by Mab414 precipitation and blotting with anti-RanGAP1 (upper) or Nup62 (lower) (n = 3).
(D) Anti-CD3-induced increase in SUMO-RanGAP1 association with the NPC is impaired in SLP-76-deficient T cells (n = 3).
(E) Anti-CD3-induced increase in SUMO-RanGAP1 association with the NPC is impaired in K56E-expressing cells. Right panel shows histogram of densitometric readings of SUMO-RanGAP1.
(F) Time course of anti-CD3-induced increase in SUMO-RanGAP1 coprecipitated by Mab414 from J14 cells expressing SLP-76 WT or K56E mutant. Anti-RanGAP1 blot (upper). Anti-SLP-76 blot of cell lysates (lower) (n = 4).