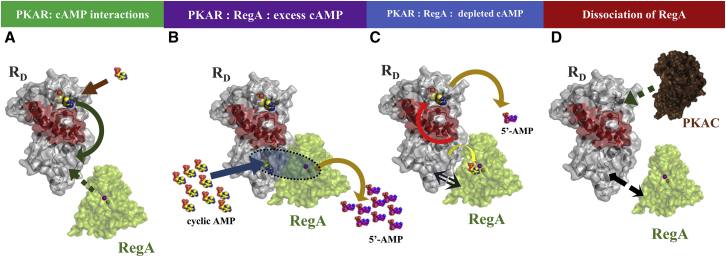
Figure 7.
Steps in PDE-mediated cAMP signal termination pathway. (A) cAMP binding at CNB:A of RD (in gray surface representation) results in an allosteric relay (green arrow) that stabilizes structural transitions in CNB:B. This presents an interaction interface for RegA (green surface representation) binding. (B) In the first step of the cAMP termination pathway, with high local cAMP (in yellow spheres) concentrations, RD and RegA form a stable catalytic complex. cAMP from the local environment binds at the RD CNB:B cAMP binding pocket and subsequently is channeled into the active site of RegA, as an example for substrate channeling in a signaling complex. (C) Once free cAMP is depleted by substrate channeling, RegA and RD form transient complexes (indicated by the black arrow). RegA binding also results in an allosteric relay (red arrow) that results in dissociation of cAMP from CNB:A. Thus RegA hydrolyzes all cAMP bound to the receptor and results in apo RD. (D) RegA dissociates from RD and subsequently primes RD to reassociate with PKAC resulting in termination of the cAMP signaling pathway. RegA, cAMP, and PKAC serve to regulate RD through unique allosteric pathways.