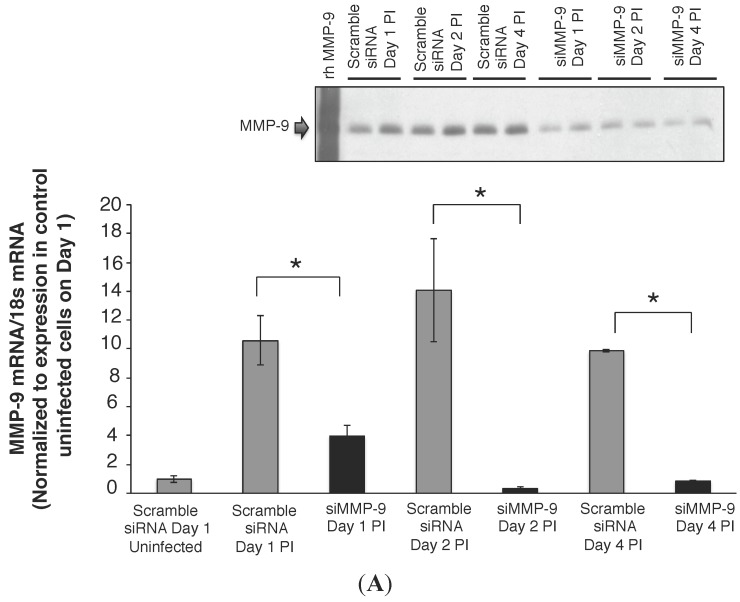
Figure 2.
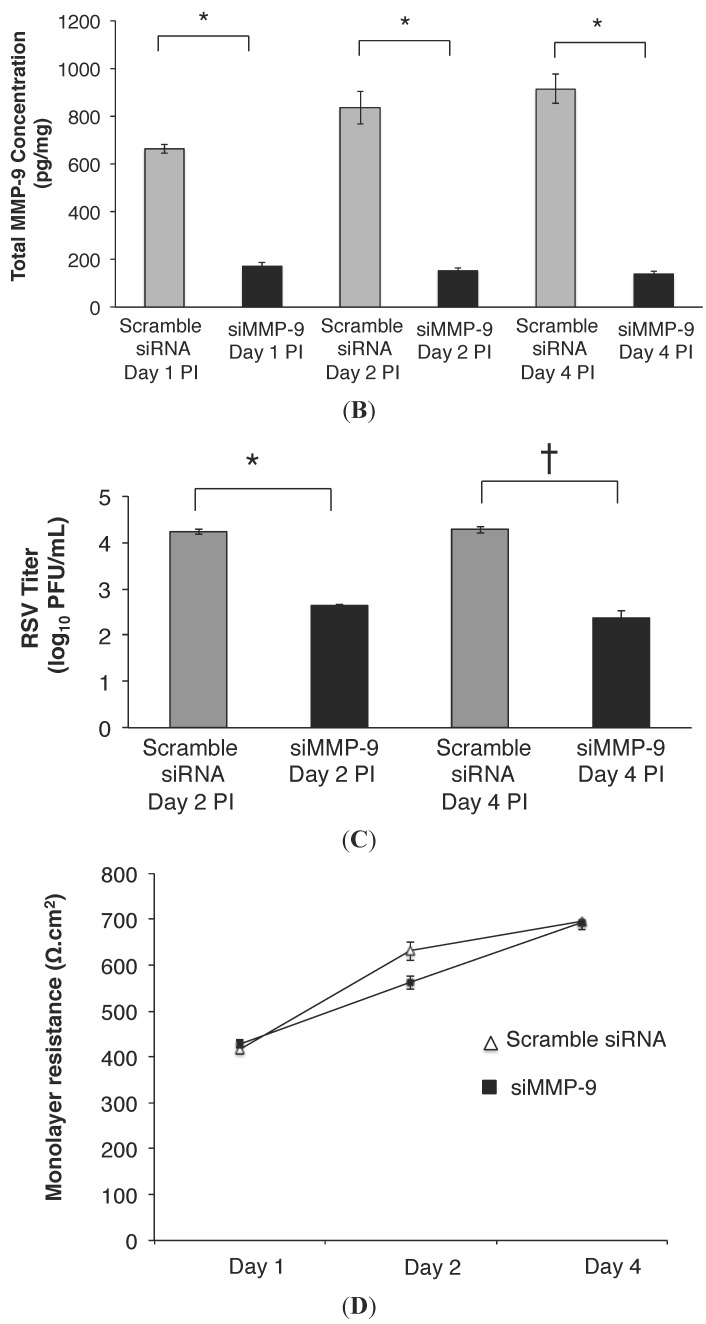
(A) MMP-9 knockdown in 16HBE cells using siRNA. RSV infection (MOI = 1) was performed 24 h post transfection with siRNA (s8864 at 10 μL; Ambion) against MMP-9. Transient transfection of siRNA s8864 resulted in knockdown of MMP-9 by 60%–80% on day1–4 PI. In contrast, cells transfected with scramble siRNA had increased MMP-9 transcription on day 1–4 PI compared to control uninfected cells, similar to our previous observation (Figure 1B). Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.0001 as indicated, by ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test. MMP-9 protein (92 kDa) detected was less in the media obtained from the apical compartment of knockdown cells (siMMP-9), compared to cells transfected with scramble siRNA. Each lane represents a sample from a separate well (Figure inset); (B) Total MMP-9 release is decreased in 16HBE cells following MMP-9 Knockdown. Total MMP-9 concentration in the apical media of HBE cells transfected with scramble siRNA (control) vs. siRNA directed against MMP-9 (siMMP-9) were measured at days 1, 2, and 4 post RSV infection (MOI = 1). On Day 1 of MMP-9 knockdown, MMP-9 levels were decreased by 74% and remained decreased by greater than 80% on days 2 and 4 post infection, compared to controls. n = 5 wells per group of experiment, at each time point. Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.00001 as indicated, by ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test; (C) RSV titer is lower in MMP-9 knockdown 16HBE cells. RSV titer was 1.6 logs lower in cells transfected with siRNA directed against MMP-9 when compared to control cells transfected with scramble siRNA (2.4 ± 0.02 log10 PFU/mL vs. 4.2 ± 0.06 log10 PFU/mL). At day 4 PI, the RSV titer remained lower in the MMP-9 knockdown cells compared to control cells (2.3 ± 0.1 log10 PFU/mL vs. 4.3 ± 0.08 log10 PFU/mL). Data represent mean ± SEM. * p < 0.00007 and † p < 0.0001 as indicated, by ANOVA followed by Tukey-Kramer multiple comparisons test; (D) Transepithelial resistance is unaffected by MMP-9 knockdown in 16HBE cells. Transepithelial resistance (TER) measurements were used as a surrogate for cell health and viability, as it requires retention of the tight junctional apparatus. We obtained TER measurements at each time point in the RSV infected HBE cells transfected with scramble siRNA (control, white triangle) and siRNA directed against MMP-9 (black square). TER measurements were similar between control and MMP-9 knockdown cells on day 1 PI. Although, the TER measurements were higher on day 2 PI in the scramble siRNA control cells, the TER measurements were similar on day 4 PI, indicating maintenance of monolayer integrity. Data represent mean ± SEM.