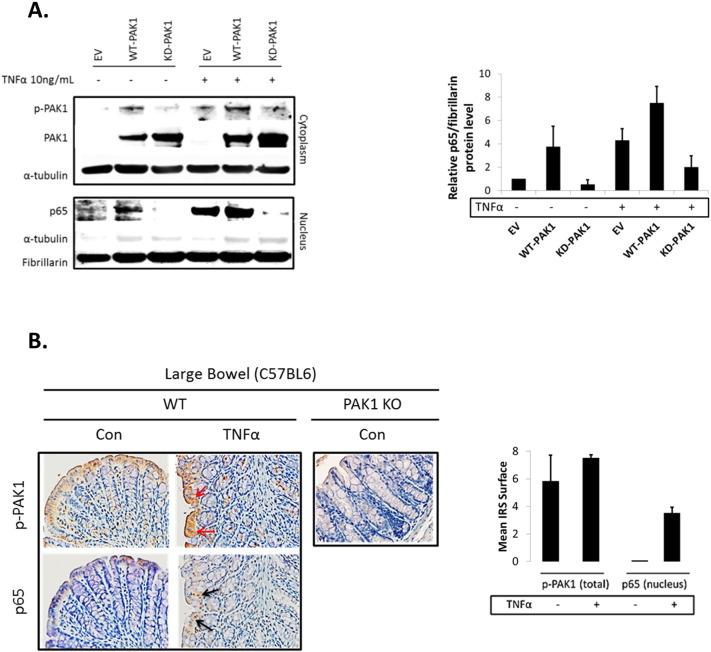
Supplementary Fig. S2.
(A–B). PAK1 overexpression regulates NF-kB activation downstream of TNFα in HCEC-1CT. (A) WB of HCEC-1CT cytoplasmic and nuclear lysates. Cells were transfected with EV, WT-PAK1 or KD-PAK1 then treated with TNFα and probed for p-PAK1, PAK1, and p65. WT-PAK1 but not KD-PAK1 overexpression increased nuclear translocation of p65. In the presence of TNFα, KD-PAK1 overexpression impedes nuclear accumulation of p65. Loading controls included α-tubulin (cytoplasm) and Fibrillarin (nucleus). Densitometry of nuclear p65 protein levels upon PAK1 overexpression in untreated or TNFα-treated cells. Data are mean and SD of 2 independent experiments. (B) IHC of p-PAK1 and p65 within large bowel tissue in TNFα injected mice. A modest increase in p-PAK1 expression (red arrows) and p65 (black arrows) nuclear translocation was observed at the luminal surface following TNFα treatment. PAK1 KO mice were stained for p-PAK1 as a negative control. Graphs show mean villi p-PAK1 and p65 IRSs (± SD) (n = 3) mice per group.