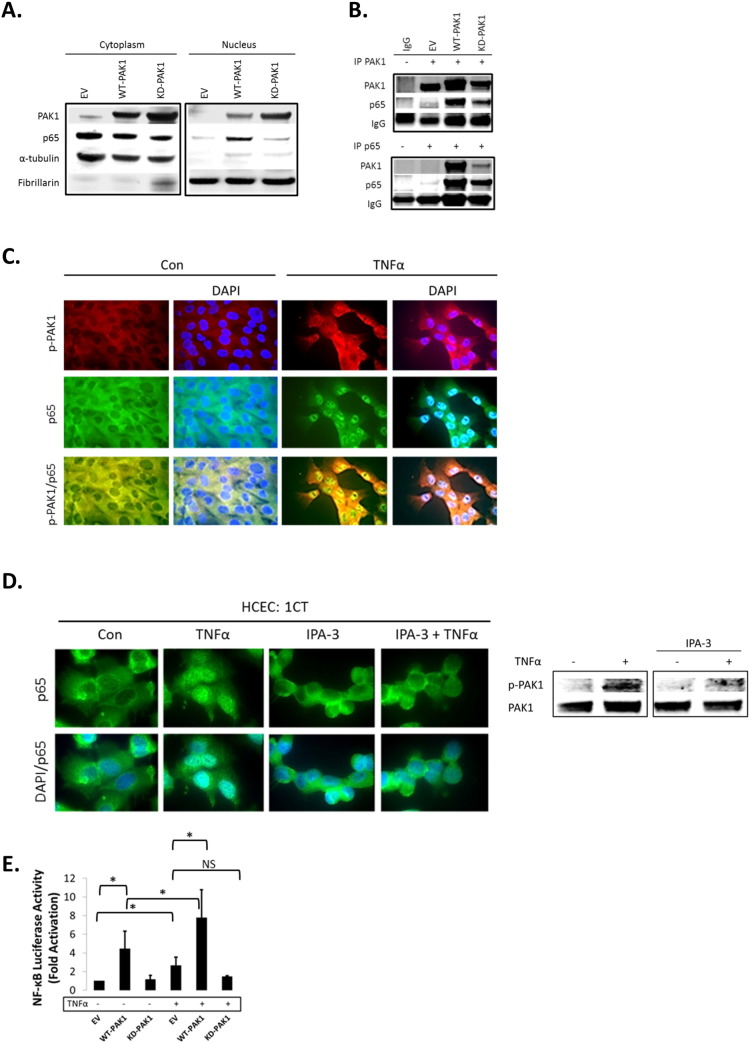
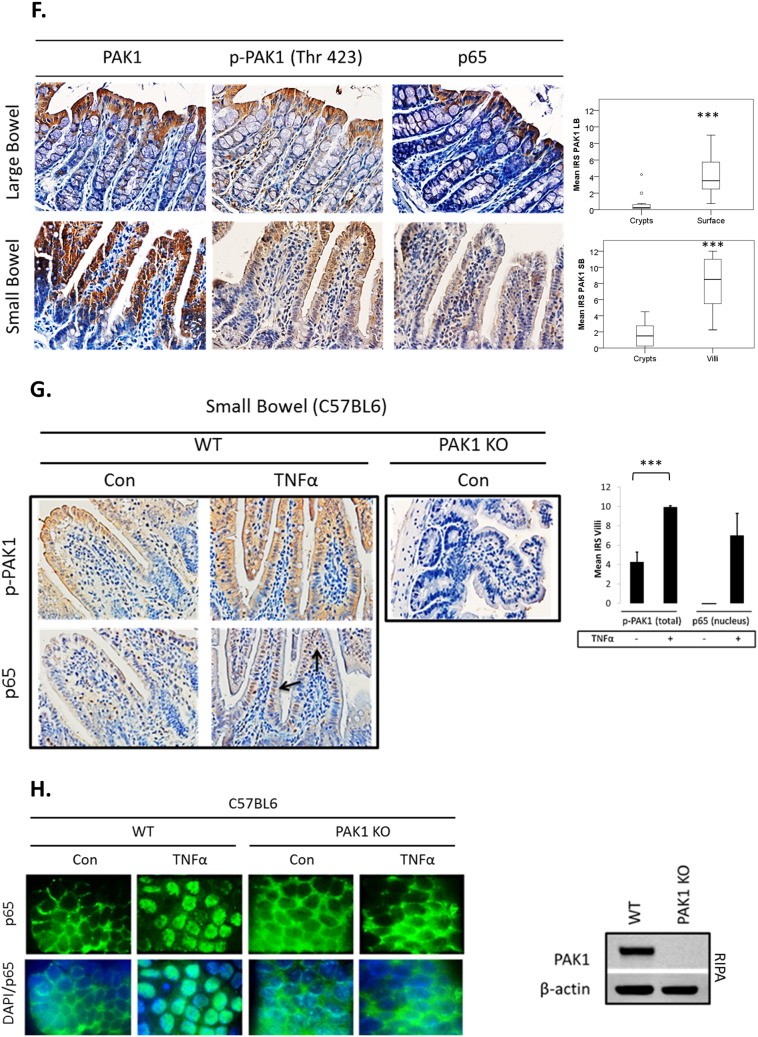
Fig. 2.
(A–H). PAK1 overexpression regulates NF-kB activation downstream of TNFα in HCEC-1CT. (A) WB of HCEC-1CT cytoplasmic and nuclear lysates. Cells were transfected with EV, WT-PAK1 or KD-PAK1 and probed for PAK1 and p65. WT-PAK1 but not KD-PAK1 overexpression increased nuclear translocation of p65. Loading controls included α-tubulin (cytoplasm) and Fibrillarin (nucleus). (B) Co-IP of PAK1 (top) and p65 (bottom) probed for PAK1 and p65 demonstrating a PAK1–p65 interaction. (C) Immunofluorescence (IF) of p-PAK1 and p65 co-staining in untreated (Con) and TNFα treated cells. Upper panel p-PAK1, middle panel p65, and lower panel merged p-PAK1/p65 images with or without merged DAPI channel. PAK1 and p65 colocalized upon TNFα. (D) IF of p65 or merged DAPI/p65 in HCEC-1CT. Cells were pre-treated with 10 μM IPA-3 (2 h) followed by 10 ng/mL TNFα for 30 min. Nuclear accumulation of p65 by TNFα is impeded by p-PAK1 inhibition. The WB verified p-PAK1 activation by TNFα and its inhibition by IPA-3 in HCEC-1CT. (E) NF-κB luciferase assay of EV, WT-PAK1, and KD-PAK1 overexpression in untreated and TNFα treated cells. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments, ANOVA, Tukey HSD; *p < 0.05. (F) Immunohistochemistry of large bowel (LB) or small bowel (SB) mouse tissue sections stained for PAK1, p-PAK1, or p65. Box plots are mean PAK1 immunoreactivity scores (IRS) comparing SB crypt and villi expression, and LB crypt and surface expression in control mice (n = 3) mice (t-test, 2 tailed; ***p < 0.001). (G) IHC of p-PAK1 and p65 within small intestinal tissue in TNFα injected mice. TNFα increases p-PAK1 expression and p65 (black arrow) nuclear translocation within villi, but not in crypts. PAK1 KO mice were stained for p-PAK1 as a negative control. Graphs show mean villi p-PAK1 and p65 IRSs (± SD) (n = 3) mice per group (t-test, 2 tailed; ***p < 0.001) (H) IF of p65 or merged DAPI/p65 in wild type (WT) and PAK1 KO mouse small intestinal organoids (SIO) with or without TNFα. WB of PAK1 protein expression in WT or PAK1 KO SIO.