Figure 2.
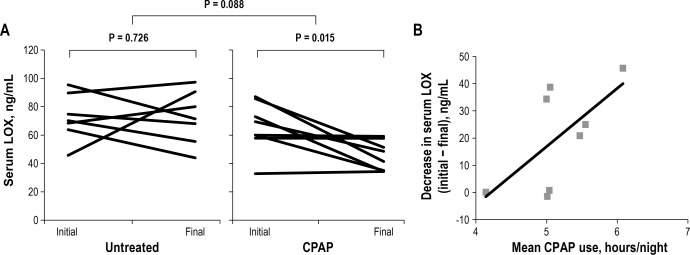
(A) Comparison of initial and final serum lysyl oxidase (LOX) values in patients with severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) who went untreated (left) and received continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy (right). Patients who received CPAP had a decline in serum LOX. Mean differences between initial and final values were 20.49 ng/mL (CPAP) and 0.19 ng/mL (control). (B) Correlation between mean nightly CPAP use and decrease in serum LOX among patients with OSA who received CPAP. R = 0.64, P = 0.084.
