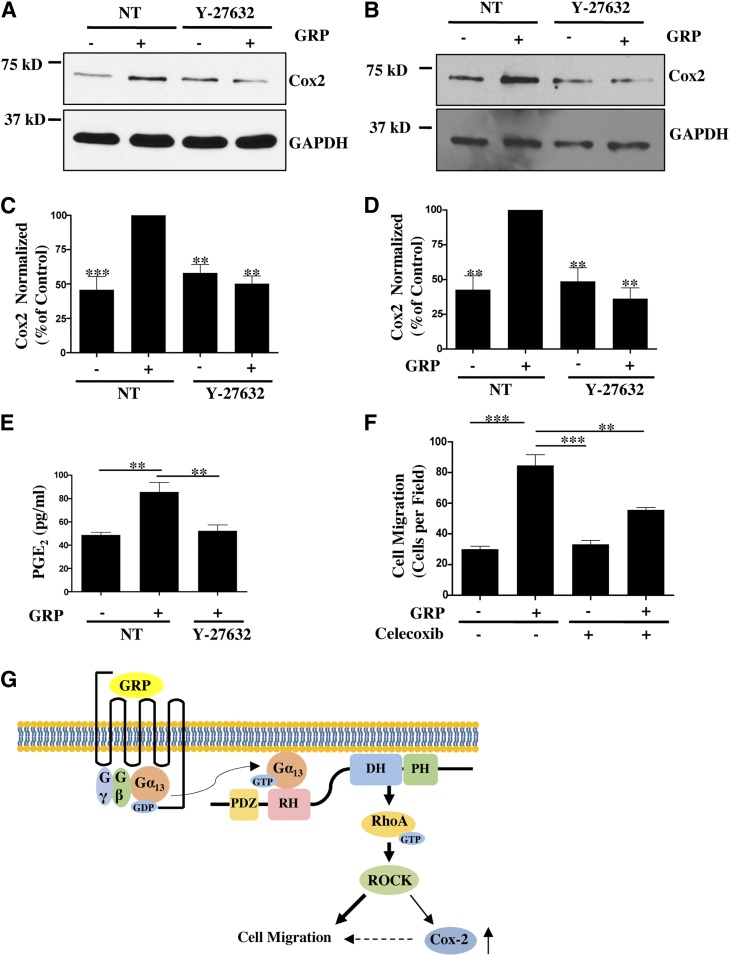
Fig. 8.
Rho-ROCK mediated regulation of Cox-2-PGE2production contributes to overall GRP stimulated cancer cell migration. (A,B) Cox-2 expression in Caco-2 (A) and HT-29 (B) cells treated with or without Y-27632 (20 μM) along with GRP for 8 hours. Cox-2 expression was verified by Western Blot. (C,D) Statistical densitometric analysis of Cox-2 expression in Caco-2 (C) and HT-29 (D) cells from n = 3. Shown are mean values ± S.E.M.; ** P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (E) Caco-2 cells serum-starved overnight and stimulated with GRP with or without Y-27632 for 8 hours. Cell media for each condition was harvested and analyzed for PGE2 concentration by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) (see Materials and Methods). Statistical analysis of n = 3. Shown are mean values ± S.E.M.; **P < 0.01. (F) Caco-2 cells serum-starved overnight and plated on the upper chamber of Transwell insert at 5 × 105 cells/well. Transwell inserts were contained in media supplemented with 1% FBS and with or without GRP along with celecoxib (20 μM) (see Materials and Methods). Statistical analysis of cell migration, n = 3 repeated in duplicates. Shown are mean values ± S.E.M.; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (G) Model of GRPR signaling in colon cancer cells. GRP stimulation increases RhoA activity primarily through Gα13-PRG activation. PRG-RhoA-ROCK signaling axis is required for GRP-stimulated colon cancer cell migration (denoted by bolder arrows). PRG-RhoA-ROCK also regulates Cox-2 expression, which makes a small contribution (denoted by dotted arrow) to overall GRP-stimulated colon cancer cell migration (see text for details).