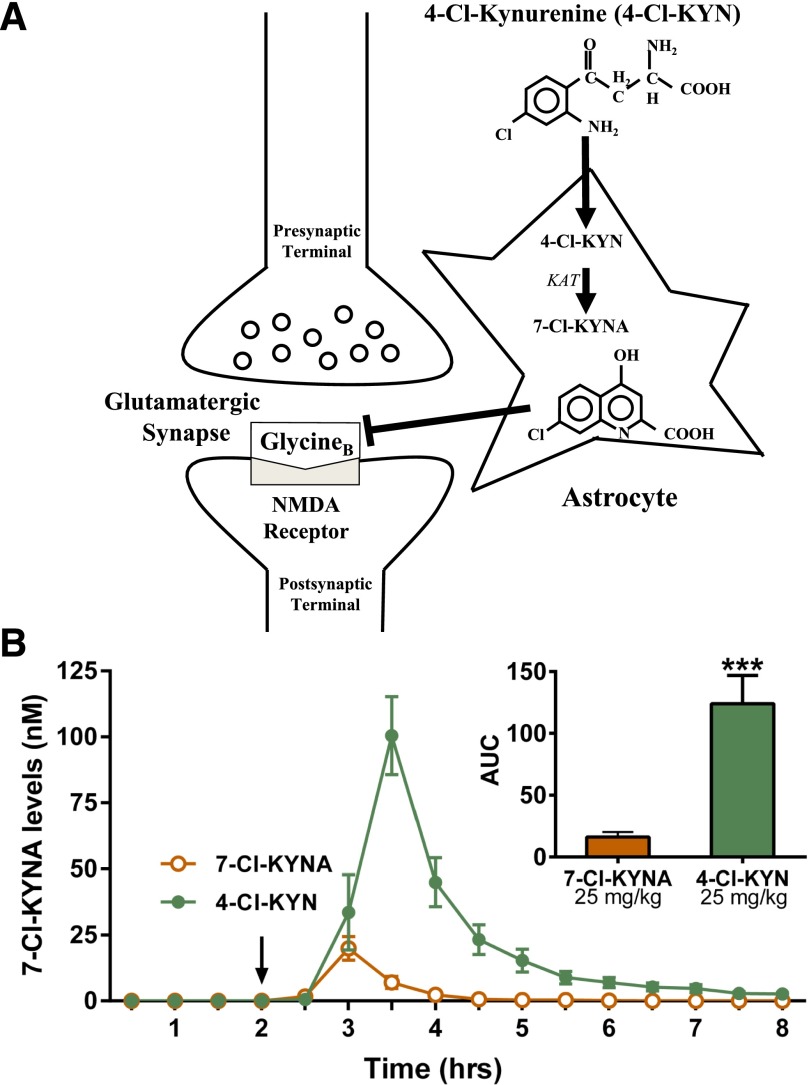
Fig. 1.
Extracellular levels of 7-chorokynurenic acid studied by microdialysis. (A) Schematic representation of 7-chlorokynurenic acid (7-Cl-KYNA) production from 4-chlorokynurenine (4-Cl-KYN) in the brain. 4-Cl-KYN readily enters the brain from the circulation and is then converted to 7-Cl-KYNA by kynurenine aminotransferase (KAT) in astrocytes. (B) Hippocampal microdialysis in freely-moving mice. The arrow indicates intraperitoneal injection of 7-Cl-KYNA (25 mg/kg) or 4-Cl-KYN (25 mg/kg). Data are the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 6/group). Inset: area under the curve (AUC); unpaired Student’s t-test. ***p < 0.001.