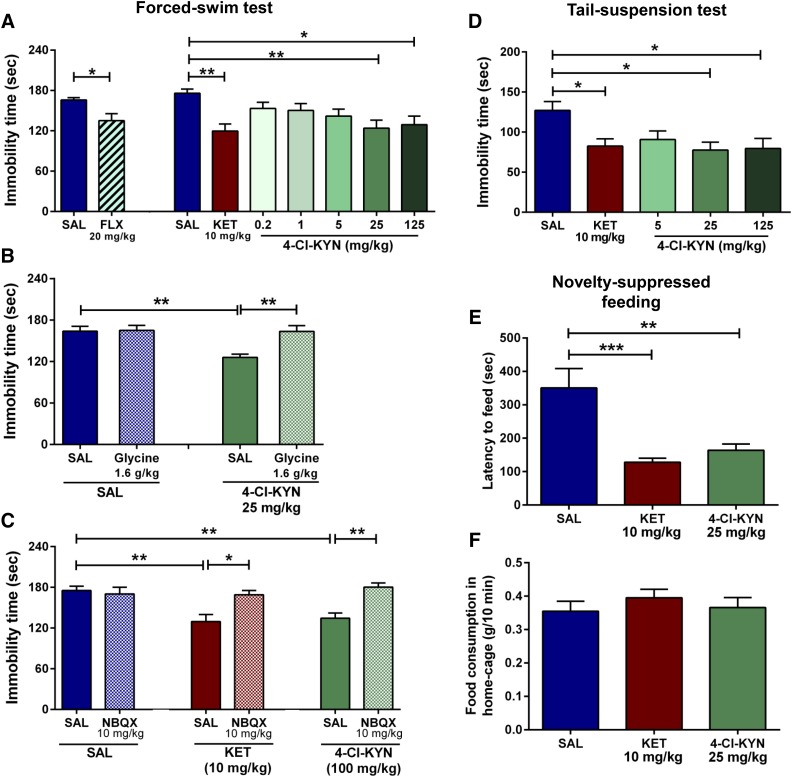
Fig. 2.
Antidepressant effects in the forced-swim, tail-suspension, and novelty-suppressed feeding tests. Mice received intraperitoneal injections of saline (SAL), fluoxetine (FLX), ketamine (KET), or 4-chlorokynurenine (4-Cl-KYN) and were tested in the FST 1-hour post-treatment. (A) Acute administration of FLX (n = 9/group; unpaired Student’s t-test) as well as KET and 4-Cl-KYN (n = 12–16/group; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison) significantly reduced immobility in the FST. (B) Glycine pretreatment prevented the antidepressant-like effects of 4-Cl-KYN in the FST (n = 13–15/group; two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison). (C) Administration of NBQX prevented the antidepressant effects of both KET and 4-Cl-KYN in the FST (n = 11–14/group, two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison). (D) In the TST, administration of 4-Cl-KYN resulted in antidepressant-like effects 1 hour postinjection (n = 16/group; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison). (E) Administration of KET and 4-Cl-KYN significantly reduced latency to feed in the NSF test, (F) without affecting home-cage food consumption (n = 10/group; one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparison). Data are the mean ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.