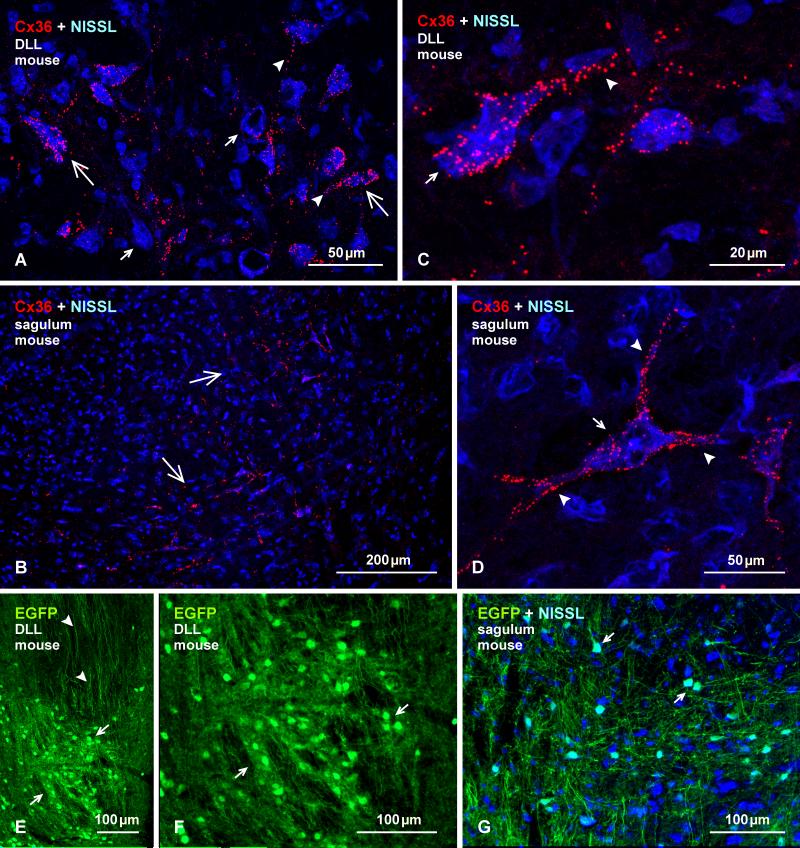
Fig. 15.
Immunofluorescence labelling of Cx36 and EGFP in the DLL and nucleus sagulum of adult mouse. (A, B) Labelling of Cx36 with blue Nissl counterstaining in the DLL (A), showing Cx36-puncta heavily concentrated on some large neuronal somata (large arrows) and their initial dendrites (arrowheads), and sparsely distributed or absent on others (small arrows). In the sagulum (B), Cx36-puncta are moderately distributed on medium sized neurons in the medial and ventromedial portions of the nucleus (arrows). (C, D) Magnification of neurons in the DLL (C) and sagulum (D), showing collections of Cx36-puncta on the surface of neuronal somata (arrows) and initial dendrites (arrowheads), which was commonly seen in DLL, but only on a few neurons per section had this density of puncta in the sagulum. (E, F) Immunolabelling of EGFP in the DLL in adult EGFP-Cx36 mice viewed at low (E) and higher (F) magnification, showing intense labelling for EGFP in neuronal cell bodies (arrows), and dense collections of dorsally located EGFP-positive axons (arrowheads). (G) The nucleus sagulum with blue Nissl counterstain, showing labelling of EGFP in a subpopulation of neurons (arrows).